- Khoa nhi
- Khoa phụ sản
- Khoa ngoại tổng hợp
- Khoa Thận Niệu - Nam khoa
- Khoa Tiêu hóa - Gan mật
- Trung Tâm Ung Bướu
- Khoa nội tổng quát
- Phòng khám răng hàm mặt
- Khoa nội tiết
- Đơn vị hồi sức sơ sinh
- Khoa mắt
- Khoa Chấn thương chỉnh hình
- Khoa tim mạch
- Khoa Vật lý trị liệu - Phục hồi chức năng
- Khoa thẩm mỹ nội khoa - Chống lão hóa
- Khoa tai mũi họng
- Khoa chẩn đoán hình ảnh
- Khoa xét nghiệm
- Khoa khám bệnh & kiểm tra sức khỏe tổng quát
- Khoa hồi sức cấp cứu
- Khoa gây mê hồi sức
- Khoa dinh dưỡng
- Đơn vị Ngoại Thần Kinh và Cột sống
- Nguyễn Hồng TrungXem thêmBook
ThS. BS. Nguyễn Hồng Trung tốt nghiệp Bác sĩ Đa khoa và Thạc sĩ Ngoại khoa tại Đại học Y Dược Huế. Bác sĩ Trung có hơn 30 năm kinh nghiệm quản lý, khám và điều trị tại các bệnh viện lớn TP.HCM. Từng giữ nhiều vị trí quan trọng như Giám đốc chuyên môn tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Hạnh Phúc, Bệnh viện Hoàn Mỹ Bình Dương. Hiện tại, ThS. BS. Nguyễn Hồng Trung đang giữ vai trò Giám đốc Y khoa tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Ong Kian SoonXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Ong Kian Soon tốt nghiệp Đại học Quốc gia Singapore năm 2004 và là Bác sĩ gia đình đã được đăng ký với Bộ Y tế Singapore. Bác có kinh nghiệm lâm sàng làm việc tại nhiều bệnh viện tư nhân và công lập ở Singapore, tại các phòng khám ngoại trú lẫn các khoa nội trú. Bác tích cực thúc đẩy quảng bá Y học gia đình tại Việt Nam và đã làm việc với Đại học Y Phạm Ngọc Thạch để đẩy mạnh y học gia đình tại TP.HCM. Bác cũng được mời làm diễn giả tại một số hội nghị y học gia đình để trao đổi về mô hình y học gia đình được thực hiện tại Singapore.
- Saijo YasuoXem thêmBook
Giáo sư - Bác sĩ Saijo Yasuo là chuyên gia hàng đầu về ung thư nội khoa với hơn 40 năm kinh nghiệm. Bác sĩ Saijo Yasuo từng giữ nhiều vị trí quan trọng tại các bệnh viện danh tiếng chuyên về ung bướu tại Nhật Bản. Từ tháng 10/2024, Bác sĩ Saijo Yasuo đảm nhiệm vai trò bác sĩ cấp cao tại Trung tâm Ung bướu Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH), nơi ông sẽ mang đến những phương pháp điều trị hiệu quả và tiên tiến với tiêu chuẩn quốc tế cho bệnh nhân tại Việt Nam. Trước khi gia nhập Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH), Giáo sư Saijo Yasuo từng giữ vai trò Trưởng khoa và Giáo sư tại Bệnh viện Đại học Y Hirosaki và Bệnh viện Đại học Tohoku. Ông đã để lại nhiều dấu ấn sâu sắc với những nghiên cứu đột phá và tâm huyết trong lĩnh vực ung bướu, đóng góp to lớn vào việc chăm sóc bệnh nhân và giáo dục y khoa.
- Mihajlovic JadrankaXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Jadranka Mihajlovic tốt nghiệp năm 2001 tại Đại học Y khoa Serbia. Bác được đào tạo chuyên sâu và có kinh nghiệm bao quát trong các lĩnh vực chuyên môn Nội khoa, Bệnh truyền nhiễm, các trường hợp Cấp cứu Nội khoa và Chấn thương. Bác đã làm việc tại các cơ sở y tế lớn nhỏ và xử lý các tình huống cấp cứu gồm tai nạn giao thông và chuyển bệnh bằng đường hàng không. Trong những năm gần đây, Bác sĩ Jadranka đặc biệt quan tâm đến việc áp dụng phương pháp tiếp cận mang tính cá nhân hóa nhiều hơn để điều trị cho bệnh nhân. Điều này bao gồm phối hợp việc thay đổi lối sống, tư vấn cải thiện sức khỏe tinh thần, kết hợp với các chất bổ sung nếu cần và tùy biến việc kê đơn thuốc phù hợp với nhu cầu riêng của từng người.
- Robert Francois Marie RicheXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Riche là chuyên gia Phẫu thuật Sản khoa với hơn 22 năm kinh nghiệm thực hành lâm sàng và giảng dạy, chuyên sâu về Ung thư vú và Phẫu thuật nội soi trong Sản phụ khoa. Bác sĩ Riche cũng dẫn dắt đội ngũ nhằm đảm bảo chất lượng khám chữa bệnh cũng như đáp ứng các cải tiến chất lượng tiêu chuẩn quốc tế thông qua các kế hoạch đào tạo và phát triển chuyên môn.
- Nguyễn Mạnh HùngXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Mạnh Hùng là Trưởng đơn vị Ngoại Thần Kinh và Cột Sống tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH). Với hơn 20 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Ngoại thần kinh và được đào tạo chuyên sâu tại Việt Nam, Pháp, Đức, Mỹ và Hàn Quốc. Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Mạnh Hùng là một trong những chuyên gia hàng đầu trong việc chẩn đoán và điều trị các bệnh lý liên quan đến hệ thần kinh trung ương, ngoại biên và cột sống, đặc biệt là các trường hợp cần can thiệp ngoại khoa phức tạp.
- Orly Attia DafniXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Orly Dafni Attia là bác sĩ nhi khoa với hơn 25 năm kinh nghiệm chăm sóc trẻ em trong nhiều lĩnh vực. Chuyên môn của bác bao gồm chẩn đoán và điều trị trẻ em mắc chứng tự kỷ, các bệnh về nhiễm trùng, các vấn đề về tăng trưởng ở trẻ em. Bác sĩ Orly đã từng công tác tại nhiều phòng khám y tế tại Hà Nội và Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh kể từ năm 2009 như Phòng khám Quốc tế Hạnh Phúc, Phòng khám Raffles Medical và Family Medical Practice.
- Nguyễn Viết ThịnhXem thêmBook
Mong muốn có thể giúp đỡ được nhiều người là động lực để Bác sĩ Chuyên khoa I Nguyễn Viết Thịnh quyết tâm thực hiện ước mơ trở thành Bác sĩ. Có cơ hội làm việc ở nhiều bệnh viện lớn, học hỏi từ các chuyên gia đầu ngành và các bác sĩ nước ngoài, Bác sĩ Chuyên khoa I Nguyễn Viết Thịnh không ngừng nỗ lực nâng cao kiến thức chuyên môn về Chấn thương chỉnh hình, tích luỹ kinh nghiệm trong từng ca bệnh và luôn tận tâm với nghề thầy thuốc cao quý.
- Esser Rene DanielXem thêmBook
GS. TS. BS. René D. Esser là Giáo sư, Bác sĩ chuyên khoa chấn thương chỉnh hình - Nguyên trưởng Khoa Đại học Stanford, USA; nguyên Trưởng Khoa Bệnh viện Markgroeningen, Tây Đức, nguyên Trưởng Khoa Chấn thương - Chỉnh hình Bệnh viện Polyclinique du Ternois, Pháp; Nguyên Trưởng khoa Chấn thương chỉnh hình, Bệnh viện Quốc Gia Tupua Tamasese Meaole, Samoa. Với bề dày hơn 40 năm kinh nghiệm, GS. TS. BS. René D. Esser là một trong số ít các bác sĩ ngoại khoa – chấn thương chỉnh hình có thể chữa trị cho những ca bệnh dị tật bẩm sinh và các bệnh lý chấn thương nghiêm trọng tại Việt Nam.
- Mai Thanh CúcXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Mai Thanh Cúc có hơn 30 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Ung bướu, hiện đang công tác tại đơn vị Ung bướu Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ. Làm việc nhiều năm trong chuyên ngành ung thư, Bác sĩ Cúc chia sẻ về phương châm của các bác sĩ chuyên khoa ung thư là lắng nghe, sẻ chia và thấu hiểu các lo lắng của bệnh nhân, bằng kiến thức và kinh nghiệm của mình giải thích cặn kẽ để bệnh nhân hiểu rõ bệnh tình của mình. Từ đó, bệnh nhân có thể chấp nhận một cách nhẹ nhàng, vững tin, hợp tác tốt với bác sĩ trong hành trình kiên trì chiến đấu để vượt qua căn bệnh nan y.
- Hồ Nguyên TiếnXem thêmBook
Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ CKI Hồ Nguyên Tiến là cựu bác sĩ nội trú Bệnh viện Antoine Beclere – APHP- Paris – Pháp năm 2008, tốt nghiệp bác sĩ nội trú Sản Phụ khoa năm 2006. Là chuyên gia phẫu thuật nội soi phụ khoa - niệu phụ khoa, thai kỳ nguy cơ cao và chẩn đoán tiền sản được đào tạo tại Việt Nam, Pháp và Singapore, với hơn 20 năm kinh nghiệm khám và điều trị chuyên ngành Sản phụ khoa - Niệu phụ khoa. Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Hồ Nguyên Tiến đã và đang không ngừng nỗ lực, thường xuyên tham gia các khóa học và hội thảo khoa học để việc cải thiện chất chăm sóc, điều trị và phẫu thuật. Với bề dày kinh nghiệm trong phẫu thuật nội soi và được đào tạo Pháp và Sigapore cũng như tại Việt Nam, Thạc Sĩ Bác sĩ Hồ Nguyên Tiến là người thực hiện các ca phẫu thuật nội soi phức tạp của Bệnh viện hiện nay, trong lĩnh vực sản khoa - chẩn đoán tiền sản là người kết nối và phát triển các mối quan hệ hợp tác giữa các khoa và các bệnh viện để đưa ra chẩn đoán chính xác cho từng trường hợp.
- Vũ Văn PhiXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ CKI Vũ Văn Phi với kinh nghiệm làm việc dày dặn 20 năm tại các bệnh viện phụ sản quốc tế lớn, từng giữ vị trí cố vấn cao cấp trong lĩnh vực sản phụ khoa và nhận được sự tín nhiệm cao từ đồng nghiệp và Quý khách hàng. Bác sĩ CKI Vũ Văn Phi rất được yêu thích trong cộng đồng mẹ bầu vì tính cách dí dỏm, tâm lý, thân thiện, giúp các bố mẹ tương lai có thể giảm bớt lo lắng trong thai kỳ. Đặc biệt Bác sĩ CKI Vũ Văn Phi nổi tiếng “mát tay”, chuyên môn cao - vết mổ đẹp và dày dạn kinh nghiệm chăm sóc các ca sinh khó, xử trí các trường hợp sản phụ mắc bệnh lý trong thai kỳ và các tai biến sản khoa thường gặp. Hiện tại, Bác sĩ CKI Vũ Văn Phi đang giữ vị trí Phó Khoa Phụ Sản, Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Vũ Nhật LinhXem thêmBook
Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ Chuyên khoa II Vũ Nhật Linh có hơn 15 năm kinh nghiệm trong ngành Y với vai trò bác sĩ Sản Phụ khoa ở nhiều bệnh viện lớn trong nước với lĩnh vực lâm sàng chuyên sâu về sản bệnh lý, hỗ trợ sinh sản, nội soi phụ khoa và đồng thời tham gia công tác giảng dạy tại Trường Đại học Y khoa Phạm Ngọc Thạch. Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ Vũ Nhật Linh là một trong những bác sĩ trẻ nhiệt huyết, tích cực đồng hành cùng các sản phụ trong hành trình chào đón thiên thần nhỏ chào đời tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ.
- Võ Bích Đại HàoXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ CKII Võ Bích Đại Hào là một bác sĩ phẫu thuật ngoại khoa hơn 25 năm kinh nghiệm phẫu thuật thành công hàng ngàn ca với tiêu chí an toàn bệnh nhân lên hàng đầu theo các chuẩn mực thực hành của Bộ Y Tế. Bác sĩ Hào nhận bằng Bác sĩ CKII tại Đại học Y Dược TP.HCM và từng học chuyên sâu về thực hành ung thư nâng cao, chẩn đoán hình ảnh, đốt khối u gan tại các trường đại học và bệnh viện lớn ở TP.HCM. Trong sự nghiệp y học của mình, bác sĩ CKII Võ Bích Đại Hào đã nhận được nhiều bằng khen danh giá như "Bàn tay vàng ngành Y", "Phẫu thuật thành công ca báo động đỏ cứu sống bệnh nhân vết thương thủng tim", "Cấp cứu thành công trường hợp đứt động mạch đùi", "triển khai kỹ thuật Phẫu thuật cắt thực quản không mở ngực, tạo hình thực quản bằng ống dạ dày ngã cổ và ngã bụng". Với phương châm luôn đặt an toàn bệnh nhân lên hàng đầu, luôn lắng nghe và theo dõi bệnh nhân sát sao trước, trong và sau phẫu thuật nhằm đảm bảo bệnh nhân đạt được kết quả điều trị tốt nhất. Hiện nay, bác sĩ CKII Võ Bích Đại Hào đang là Trưởng khoa Ngoại tổng quát tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Nguyễn Ngọc TiếnXem thêmBook
Là chuyên gia Niệu khoa được đào tạo tại Việt Nam, Pháp và Bỉ, với hơn 35 năm kinh nghiệm khám và điều trị chuyên ngành Niệu khoa và quản lý y tế. Tiến Sĩ Bác sĩ Nguyễn Ngọc Tiến đã và đang không ngừng nỗ lực đóng góp vào việc cải thiện chất lượng dịch vụ y tế tại Việt Nam. Với bề dày kinh nghiệm quốc tế tại Pháp và Bỉ cũng như tại Việt Nam, Tiến Sĩ Bác sĩ Tiến là người có vai trò quan trọng trong quá trình xây dựng và thành lập Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH) hiện nay, đặc biệt là trong việc kết nối và phát triển các mối quan hệ hợp tác chiến lược giữa AIH và các hệ thống y tế hàng đầu tại Mỹ (Johns Hopkins International, Dignity Health international). Tiến Sĩ Bác sĩ Nguyễn Ngọc Tiến, Thành viên HĐQT kiêm cố vấn Y Khoa của Bệnh Viện AIH.
- Trương Dạ UyênXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Trương Dạ Uyên sở hữu hơn 25 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực khám sức khỏe tổng quát, đặc biệt có chuyên môn sâu trong công tác điều trị các bệnh về nội tiết. Trong sự nghiệp cống hiến của mình, Bác sĩ Trương Dạ Uyên đã có nhiều bài viết về các bệnh lý nội tiết trên các tạp chí y khoa và đạt được nhiều thành tựu và giải thưởng. Bác sĩ còn là thành viên của các Hiệp hội nội tiết và điều trị tiểu đường trong nước và quốc tế. Đối với bệnh nhân, bác sĩ Trương Dạ Uyên được biết đến như một thiên thần áo trắng giỏi chuyên môn, giàu kinh nghiệm và đặc biệt là phong cách phục vụ dịu dàng, tận tâm. Bác sĩ Trương Dạ Uyên hiện đang giữ chức vụ Trưởng Khoa Khám bệnh & Kiểm tra sức khỏe tổng quát tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Nguyễn Thịnh VượngXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Nguyễn Thịnh Vượng tốt nghiệp Đại học Y Dược Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh loại ưu năm 1995, sau đó lấy bằng cử nhân Anh ngữ năm 1998. Trải qua 30 năm công tác, Bác sĩ Nguyễn Thịnh Vượng không ngừng học tập và đã hoàn tất chương trình đào tạo chuyên khoa sau đại học về hai chuyên ngành cấp cứu và nội tiết học; đặc biệt giàu kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực chăm sóc và điều trị đái tháo đường. Năng động và nhiệt huyết trong cập nhật kiến thức y khoa, Bác sĩ Nguyễn Thịnh Vượng đã tham dự nhiều hội nghị khoa học tại Mỹ. Bác sĩ Nguyễn Thịnh Vượng cũng là thành viên của Hiệp hội Cấp cứu Hoa Kỳ và Hội Nội tiết Hoa Kỳ. Hiện nay bác Vượng là Bác sĩ Nội tiết kiêm phụ trách khám sức khỏe tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Strati Julian AlbertoXem thêmBook
Dr. Julian Strati, một bác sĩ y khoa người Argentina, có hơn 15 năm kinh nghiệm chuyên sâu về chăm sóc tích cực (ICU), bao gồm 5 năm quản lý ICU. Bác sĩ Julian có kinh nghiệm sống và làm việc tại Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh, Việt Nam hơn 6 năm. Bác Julian nổi bật trong lĩnh vực chăm sóc hô hấp, với chuyên môn về thông khí cơ học (thở máy), nội soi phế quản và phục hồi sau thông khí cơ học. Ông cũng có chuyên môn trong các thủ thuật như mở khí quản qua da và xử lý rối loạn dây thanh quản sau khi đặt nội khí quản. Trong suốt sự nghiệp của mình, ông đã giữ các vai trò quan trọng tại các bệnh viện ở Buenos Aires như Bệnh viện Interzonal General de Agudos Guemes de Haedo; Clinica Olivos, Swiss Medical Group và Hệ thống phòng khám Family Medical Practice, tại Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh. Với nền tảng học vấn vững chắc từ Đại học Buenos Aires và các chuyên ngành nâng cao về chăm sóc tích cực và phổi, bác Julian luôn nỗ lực học hỏi liên tục và cung cấp dịch vụ chăm sóc bệnh nhân tốt nhất trong lĩnh vực y học chăm sóc tích cực.
- Bùi Thị Thùy TâmXem thêmBook
Là một bác sĩ tâm huyết với tình yêu lớn lao dành cho trẻ, Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Bùi Thị Thùy Tâm đang công tác tại Khoa Nhi - Sơ sinh, Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ. Với hơn 15 năm kinh nghiệm thực tiễn, đã từng công tác tại Bệnh viện Nhi Đồng, với lĩnh vực lâm sàng chuyên sâu là Nhi tổng quát và sơ sinh, bác sĩ Tâm luôn không ngừng học hỏi và hoàn thiện bản thân. Bên cạnh chuyên môn vững vàng và tinh thần trách nhiệm cao, bác sĩ Tâm còn được yêu mến vì sự thân thiện, nhẹ nhàng, hết lòng vì các bệnh nhi.
- Trần Hải ĐăngXem thêmBook
Với hơn 25 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực chẩn đoán hình ảnh, Bác sĩ Trần Hải Đăng đã công tác tại nhiều bệnh viện và phòng khám uy tín như Vinmec, Việt Pháp, Hữu Nghị, và Phòng khám Quốc tế SOS. Đặc biệt, bác sĩ còn đồng hành từ những ngày đầu tiên trong quá trình thành lập Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ. Tốt nghiệp Đại học Y Hà Nội, Bác sĩ Hải Đăng tiếp tục hoàn thiện chuyên môn tại Pháp thông qua các chương trình đào tạo chuyên sâu về chẩn đoán X-quang và hình ảnh y học tại Đại học Reims và Đại học Clermont-Ferrand. Bác cũng đạt được nhiều chứng chỉ quan trọng như điện quang can thiệp và siêu âm Doppler tại Thụy Sĩ, cùng các chứng nhận uy tín từ Hội Điện quang Bắc Mỹ và Pháp. Hiện tại, bác đang đảm nhận vai trò Trưởng khoa Chẩn đoán hình ảnh tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Nguyễn Thị Ngọc LanXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ CKII Nguyễn Thị Ngọc Lan có bề dày hơn 35 năm kinh nghiệm khám và điều trị các bệnh lý chuyên sâu về Sản Phụ Khoa đặc biệt là chăm sóc thai kỳ nguy cơ cao tại các bệnh viện lớn tại TP. HCM. Với phương châm: "Trao niềm tin - Đón bình an", bác sĩ Ngọc Lan luôn tận tâm với nghề, đặt sức khỏe và bình an của bệnh nhân lên trên hết. Bằng sự vui vẻ, nhẹ nhàng, tâm lý, bác sĩ mang lại cảm giác thoải mái, gần gũi và an tâm cho khách hàng và gia đình. Với nỗ lực trau dồi không ngừng, bác sĩ CKII Nguyễn Thị Ngọc Lan nhận nhiều chứng chỉ đào tạo bài bản và chuyên sâu không chỉ ở Việt Nam mà còn từ các chương trình huấn luyện và hợp tác đào tạo quốc tế với các bệnh viện và trường y khoa tại Pháp. Động lực lớn nhất giúp bác sĩ Ngọc Lan luôn giữ được đam mê với nghề và cống hiến hết mình đến nay chính là sự tin yêu của các gia đình trong vai trò “ Bà đỡ mát tay, may đẹp”.
- Nguyễn Thị Như ÁiXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Nguyễn Thị Như Ái có hơn 30 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực phục hồi chức năng, đặc biệt có chuyên môn sâu về phục hồi chức năng tim mạch, phục hồi chức năng cho bệnh nhân tai biến mạch máu não và luôn không ngừng nâng cao, cập nhật kiến thức chuyên môn. Bác sĩ Nguyễn Thị Như Ái hiện đang đảm nhận vai trò Trưởng Khoa Phục hồi chức năng tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ.
- Dương Thúy LiênXem thêmBook
Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Dương Thúy Liên có hơn 40 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Nội tổng quát, đặc biệt có chuyên môn sâu về bệnh lý van tim và bệnh tim bẩm sinh. Trong sự nghiệp của mình, với những đóng góp trong công tác điều trị chuyên môn và nghiên cứu y khoa, Bác sĩ Dương Thúy Liên đã được phong tặng danh hiệu "Thầy thuốc ưu tú". Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Dương Thúy Liên hiện đang đảm nhận vị trí Trưởng Khoa Nội Tổng quát tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ.
- Trần Thị Khuê VyXem thêmBook
Với hơn 35 năm kinh nghiệm làm việc và đào tạo nâng cao ở trong nước và nước ngoài, Bác sĩ Chuyên khoa tim mạch Trần Thị Khuê Vy sở hữu năng lực chuyên môn và một bề dày kinh nghiệm khiến nhiều người ngưỡng mộ. Nền tảng kiến thức trong nước vững vàng, có thể sử dụng tốt tiếng Pháp và tiếng Anh, Bác sĩ Trần Thị Khuê Vy đã có thời gian tu nghiệp thực hành nội trú và nhận bằng liên đại học về siêu âm tim mạch cũng như các chứng chỉ chuyên ngành tim mạch khác tại Pháp. Bác sĩ Vy cũng từng tham gia các chương trình đào tạo quốc tế ngắn hạn và hội nghị y khoa ở nước ngoài. Hiện bác sĩ đang là công tác tại Khoa tim mạch tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ.
- Trần Thu PhượngXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Trần Thu Phượng có hơn 30 năm kinh nghiệm công tác trong lĩnh vực chẩn đoán hình ảnh ở các bệnh viện lớn tại Tp. Hồ Chí Minh (Bệnh viện An Bình, FV), đặc biệt có thế mạnh về các thủ thuật chẩn đoán hình ảnh, hỗ trợ đắc lực trong việc chẩn đoán và điều trị cho bệnh nhân. Bác sĩ Phượng đã được đào tạo nội trú về chuyên khoa Chẩn đoán hình ảnh chuyên sâu tại các bệnh viện tại Pháp: Bệnh viện Beaujon (Paris), Bệnh viện trường đại học Montpellier, Bệnh viện trường đại học Tours và tại Australia. Bác sĩ Phượng có thời gian giảng dạy các lớp định hướng Bác sĩ Chẩn đoán hình ảnh tại trường Đại học Y khoa Phạm Ngọc Thạch. Với niềm đam mê và mong muốn cống hiến cho ngành y, bác sĩ Trần Thu Phượng không ngừng trau dồi tri thức khi tham gia nhiều khóa đào tạo chuyên sâu về Chẩn đoán hình ảnh trong và ngoài nước và đạt nhiều giải thưởng tại các cuộc thi Nghiên cứu Khoa học. Hiện nay, Bác sĩ Trần Thu Phượng là Bác sĩ Phó khoa Chẩn đoán hình ảnh - Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Nguyễn Thị Diệu VyXem thêmBook
Với hơn 10 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực hồi sức tích cực, Bác sĩ CKII Nguyễn Thị Diệu Vy đã gặt hái những thành tựu như Bác sỹ Trẻ Giỏi Bệnh viện Trưng Vương và Bác sỹ tích cực tham gia chống dịch vì cộng đồng do Ủy ban Nhân dân TPHCM trao tặng. Bác sĩ Diệu Vy đã từng công tác tại các bệnh viện lớn như Bệnh viện Quận 4, Bệnh viện Trưng Vương. Hiện tại, Bác sĩ CKII Nguyễn Thị Diệu Vy đang giữ vị trí Bác sĩ Hồi sức cấp cứu tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Nguyễn Đình MỹXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ CKII Nguyễn Đình Mỹ nguyên là Trưởng khoa Tai Mũi Họng Bệnh viện Nguyễn Trãi, bệnh viện Hạng I tại TP.HCM, từng tham gia đào tạo thực hành lâm sàng cho nhiều thế hệ Bác sĩ trẻ chuyên khoa Tai – Mũi - Họng. Với hơn 30 năm kinh nghiệm khám chữa bệnh ở chuyên khoa Tai - Mũi - Họng cùng nhiều công trình nghiên cứu và bài báo chuyên môn được xuất bản, Bác sĩ CKII Nguyễn Đình Mỹ hiện nay đang công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ với vai trò Bác sĩ Tai Mũi Họng.
- Quách VănXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Quách Văn có hơn 10 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Sản phụ khoa, chuyên sâu về chăm sóc thai kỳ, phẫu thuật sản phụ khoa, điều trị các bệnh lý phụ khoa, tư vấn và điều trị hiếm muộn, vô sinh, biện pháp kế hoạch hóa gia đình. Bác sĩ Quách Văn cũng tham gia nghiên cứu và được huấn luyện chuyên sâu về Sản khoa và Phụ khoa tại Đại học Y Khoa Phạm Ngọc Thạch, Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh và hoàn thành nhiều khóa đào tạo Chuyên Phụ Khoa tại Bệnh viện Từ Dũ. Bác sĩ Quách Văn nguyên là Trưởng khoa Sản phụ khoa, Bệnh viện Quận 6 và hiện đang công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).Enable GingerCannot connect to Ginger Check your internet connectionor reload the browserDisable in this text fieldRephraseRephrase current sentenceEdit in Ginger×
- Nguyễn Tam Xuân KiệtXem thêmBook
BS.CKI Nguyễn Tam Xuân Kiệt tốt nghiệp Bác sĩ đa khoa tại Trường Đại học Y khoa Phạm Ngọc Thạch và hoàn thành chương trình Chuyên khoa I - Hồi sức Cấp cứu - Chống độc vào năm 2023. Với hơn 6 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực cấp cứu và hồi sức, bác sĩ đã từng công tác tại nhiều bệnh viện và tổ chức y tế lớn như Trung tâm Cấp cứu 115 TPHCM, Tổ chức International SOS, Bệnh viện Gia An 115,… Đặc biệt, từ tháng 5/2024, bác sĩ đã đồng hành cùng Bệnh viện Quốc Tế Mỹ (AIH) với vai trò Bác sĩ Cấp cứu & Hồi sức bán thời gian. Hiện nay, bác sĩ chính thức đảm nhận vị trí Bác sĩ Cấp cứu & Hồi sức toàn thời gian tại AIH, tiếp tục mang đến sự tận tâm và chuyên môn vững vàng trong công tác điều trị khẩn cấp.
- Trần Hồng PhúcXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Trần Hồng Phúc là bác sĩ chuyên khoa gây mê hồi sức với gần 30 năm kinh nghiệm làm việc trong nước và quốc tế. Bác sĩ Trần Hồng Phúc từng có thời gian tham gia đào tạo về chuyên khoa gây mê tại Đại học Paris V – Rene Descartes và là bác sĩ gây mê nội trú tại Bệnh viện Beaujon, Paris, Pháp. Với nền tảng chuyên môn sâu rộng, kinh nghiệm quốc tế, Bác sĩ Trần Hồng Phúc hiện nay đang là Phó Trưởng khoa Gây mê hồi sức Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Vũ Việt VânXem thêmBook
Được đào tạo y khoa tại Việt Nam, Mỹ và Úc, Bác sĩ CK I Vũ Việt Vân đã có nhiều năm kinh nghiệm làm việc tại các bệnh viện và cơ sở y tế của Việt Nam và Mỹ. Bác sĩ Vân hiện đang là bác sĩ chẩn đoán hình ảnh tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH) với lĩnh vực lâm sàng chuyên sâu: Siêu âm (sản phụ khoa/vú, tổng quát, Doppler, cơ-xương-khớp), X-quang.
- Huỳnh Hoàng AnhXem thêmBook
ThS.BS.CKI Huỳnh Hoàng Anh tốt nghiệp Bác sĩ đa khoa tại Trường Đại học Y Dược TPHCM năm 2009 và tiếp tục hoàn thành Thạc sĩ Nhi khoa vào năm 2013. Với hơn 15 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Nhi khoa, bác sĩ đã từng công tác tại nhiều bệnh viện lớn như Bệnh viện Nhi Đồng 2, Bệnh viện Pháp Việt, và đặc biệt đã đồng hành cùng Bệnh viện Quốc Tế Mỹ ngay từ những ngày đầu thành lập, góp phần xây dựng và phát triển môi trường y tế chất lượng cao, mang đến sự chăm sóc tận tâm và toàn diện cho các bệnh nhi.
- Lê Thị Thanh Loan
- Lê Thi Thanh LiêmXem thêmBook
Là một nữ Bác sĩ của khoa Nhi với lòng yêu nghề và yêu trẻ, Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Lê Thị Thanh Liêm đã có hơn 15 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực lâm sàng chuyên sâu Nhi sơ sinh. Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Lê Thị Thanh Liêm không ngừng học hỏi, trao dồi chuyên môn, tham gia nhiều chương trình quốc tế về đào tạo chuyên khoa và đào tạo sau đại học hợp tác với các tổ chức quốc tế Hoa Kỳ, Úc… Hiện nay Bác sĩ Lê Thị Thanh Liêm đang công tác tại Khoa Nhi - Sơ sinh, Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ.
- Trần VõXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Trần Võ với hơn 6 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Nhi - Sơ sinh, được đào tạo chuyên môn bác sĩ Đa khoa, Bác sĩ CKI tại Đại Học Y Dược TP.HCM và hoàn thành nhiều bằng cấp chứng chỉ đào tạo liên tục tại Bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy. Hiện tại Bác sĩ Trần Võ đang giữ vai trò bác sĩ Nhi & Sơ sinh - Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Trần Thị LamXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Trần Thị Lam có hơn 15 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vưc Nhi – Sơ sinh và hiện đang công tác tại khoa Nhi – Sơ sinh, Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH). Trong quá trình công tác thường xuyên tiếp xúc và điều trị các trẻ sơ sinh có vấn đề bệnh lý như non tháng, nhiễm trùng, có vấn đề ngoại khoa, dị dạng, Bác sĩ Trần Thị Lam luôn thể hiện bản lĩnh và chuyên môn cao của một bác sĩ giàu kinh nghiệm, nhiệt huyết và tận tâm. Bác sĩ Trần Thị Lam cũng có những nghiên cứu, báo cáo khoa học đáng ghi nhận được đăng trên các tạp chí y học uy tín.
- Nguyễn Thái TrânXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Thái Trân là một chuyên gia giàu kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Y học Gia đình và Nội tổng quát, hiện đang công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH). Ngoài nền tảng học vấn vững chắc, bác sĩ còn tham gia nhiều khóa đào tạo chuyên sâu, như Quản lý Hen và COPD trong cộng đồng, kỹ năng đọc điện tâm đồ, quản lý bệnh lý tuyến giáp và đái tháo đường công cộng, và có chứng chỉ tâm thần học cơ bản. Với kinh nghiệm làm việc đa dạng từ các phòng khám quốc tế như Phòng khám Gia đình Tokyo và Careplus, cho đến các bệnh viện lớn như Bệnh viện Bình Thạnh và Bệnh viện Phạm Ngọc Thạch, bác sĩ Thái Trân luôn không ngừng trau dồi kiến thức và kỹ năng để mang lại dịch vụ chăm sóc sức khỏe tốt nhất cho bệnh nhân.
- Trần Thị Thu ThảoXem thêmBook
Là Bác sĩ Chuyên khoa da liễu với kiến thức chuyên môn sâu qua nhiều năm kinh nghiệm trong nghề và quá trình không ngừng phấn đấu bổ sung kỹ năng chuyên môn trong lĩnh vực da liễu và thẩm mĩ nội khoa công nghệ cao ở nhiều nước có công nghệ thẩm mỹ phát triển như Hàn Quốc, Thái Lan, Malaysia, Bác sĩ Chuyên khoa I Trần Thị Thu Thảo hiện đang là Bác sĩ Da liễu công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ.
- Dương Xuân Nguyện
- Ngô Thanh Mai
- Hoàng Thọ Khánh ToànXem thêmBook
Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Hoàng Thọ Khánh Toàn có hơn 10 năm kinh nghiệm làm việc về chuyên khoa Nội tim mạch với nhiều năm công tác trong môi trường bệnh viện quốc tế chất lượng cao. Hiện tại, Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Hoàng Thọ Khánh Toàn đang công tác tại Khoa Nội tổng quát Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH) với vai trò bác sĩ Nội tim mạch.
- Nguyễn Thị Hồng HuyênXem thêmBook
Với hơn 10 năm học tập, nghiên cứu với lĩnh vực lâm sàng chuyên sâu là Nhi hô hấp, Thạc sĩ Bác sĩ Nguyễn Thị Hồng Huyên luôn hết lòng vì bệnh nhân nhi, đem lại sự an tâm và tin tưởng cho các bậc phụ huynh khi đưa con đến điều trị và thăm khám. Hiện nay Bác sĩ Nguyễn Thị Hồng Huyên hiện đang công tác tại Khoa Nhi - Sơ sinh, Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Huỳnh Thị Bạch TuyếtXem thêmBook
Có gần 20 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Sản phụ khoa, Bác sĩ Huỳnh Thị Bạch Tuyết sở hữu kiến thức chuyên môn vững chắc với thế mạnh về bệnh lý ung bướu phụ khoa, chăm sóc thai kỳ nguy cơ cao và nội tiết trong sản phụ khoa. Bác sĩ Huỳnh Thị Bạch Tuyết cũng tham gia công tác giảng dạy và có kinh nghiệm 10 năm làm Giảng viên Bộ môn Sản Phụ khoa tại Đại học Y khoa Phạm Ngọc Thạch. Bác sĩ Huỳnh Thị Bạch Tuyết hiện đang là bác sĩ Sản phụ khoa tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Lã Thị Bạch LýXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Lã Thị Bạch Lý có hơn 15 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Truyền nhiễm và các Bệnh Nhiệt đới, với lĩnh vực lâm sàng chuyên sâu trong điều trị Viêm gan siêu vi B, C; Chẩn đoán, điều trị và dự phòng lây nhiễm HIV (trước và sau phơi nhiễm). Hiện nay bác sĩ Lý đang là bác sĩ Nội nhiễm tại Khoa Nội tổng quát, Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ.
- Quách Triều GiangXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Quách Triều Giang tốt nghiệp Đại học Y khoa Phạm Ngọc Thạch và đã từng công tác tại Bệnh viện Phục hồi chức năng Điều trị bệnh nghề nghiệp, Bệnh viện Nhân dân 115. Hiện nay bác sĩ Giang đang cộng tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH) với vai trò Bác sĩ ngoại tổng quát kiêm hỗ trợ bác sĩ ngoại viện. Luôn hướng tới sự chuyên nghiệp trong chăm sóc sức khỏe, bác sĩ Giang không ngừng nâng cao chuyên môn, mong muốn mang đến quá trình điều trị nhẹ nhàng, hiệu quả, an toàn và ít xâm lấn. Quan điểm khám và chữa bệnh của bác sĩ Giang là cá thể hóa việc điều trị cho từng bệnh nhân. Mỗi bệnh nhân đều là một cá thể khác biệt, có câu chuyện riêng cần được lắng nghe và thấu hiểu, từ đó đưa ra hướng điều trị phù hợp nhất. “Được chăm sóc sức khỏe, giúp đỡ bệnh nhân chính là điều quý giá và thiêng liêng.” – Bác sĩ Giang chia sẻ.
- Trần Thị Phượng HằngXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Trần Thị Phượng Hằng tốt nghiệp Đại học Y Dược TP.HCM và đã từng công tác tại Bệnh viện Bà Rịa. Luôn hướng tới sự chuyên nghiệp trong chăm sóc sức khỏe, bác sĩ Hằng không ngừng nâng cao chuyên môn, mong muốn mang đến quá trình chăm sóc và điều trị thật hiệu quả với các khóa đào tạo liên tục tại Bệnh viện Từ Dũ. Hiện nay bác sĩ Hằng đang cộng tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH) với vai trò Bác sĩ Sản phụ khoa.
- Nguyễn Phương NamXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Nguyễn Phương Nam với hơn 10 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực sản phụ khoa, được đào tạo chuyên môn bác sĩ đa khoa và bác sĩ chuyên khoa phụ sản tại Đại Học Y Dược Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh. Không ngừng nâng cao chuyên môn, Bác sĩ Nguyễn Phương Nam đã tham gia nhiều khóa học, tập huấn về chuyên ngành sản phụ khoa. Bác sĩ Nguyễn Phương Nam có nhiều năm công tác tại bệnh viện Thủ Đức và bệnh viện Hùng Vương và hiện đang công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Nguyễn Quang DuyXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Quang Duy với hơn 5 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực cấp cứu và hồi sức tích cực, được đào tạo chuyên môn bác sĩ đa khoa và bác sĩ chuyên khoa I tại Đại học Y Khoa Phạm Ngọc Thạch. Không ngừng nâng cao chuyên môn, Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Quang Duy đã tham gia nhiều khóa học, tập huấn về chuyên ngành như Lọc máu ngoài cơ thể và Kiểm soát Hen COPD. Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Quang Duy đã từng công tác tại bệnh viện Đa khoa Lê Văn Việt và bệnh viện Đa khoa Hồng Đức TP.HCM và hiện đang giữ vị trí Bác sĩ Cấp cứu và Hồi sức tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Hồ Ngọc Bảo TrânXem thêmBook
Thạc sĩ Hồ Ngọc Bảo Trân là chuyên gia tâm lý đã tốt nghiệp và được đào tạo ở Đại học Khoa học Xã hội và Nhân văn. Với nhiều chứng chỉ và kinh nghiệm quý báu nhiều năm công tác tại các Trường Đại học, Trung tâm tâm lý lâm sàng, Thạc sĩ Hồ Ngọc Bảo Trân hiện đang giữ vai trò Chuyên viên tư vấn tâm lý Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Ngô Vũ Bích NgọcXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Ngô Vũ Bích Ngọc có hơn 10 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Cấp cứu và hồi sức Nhi khoa, Nhi tổng quát, Nhi sơ sinh, từng công tác tại các bệnh viện lớn như Bệnh viện Nhi đồng, Vinmec. Hiện nay bác sĩ Ngọc đang công tác tại Khoa Nhi và Hồi sức Sơ sinh – Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH). Đối với bác sĩ Ngọc, nghề Y mang sứ mệnh rất thiêng liêng, và người thầy thuốc sẽ góp phần phục vụ và nâng đỡ người bệnh trong những giai đoạn bất an của họ về tinh thần và sức khoẻ. Vì vậy bác sĩ Ngọc không ngừng nâng cao trình độ, luôn cập nhật kiến thức để mang lại dịch vụ chăm sóc đúng nhất và tốt nhất cho người bệnh. Đồng thời quan điểm chăm sóc bệnh nhân của bác sĩ Ngọc là “Lương y như từ mẫu”, bên cạnh kiến thức chuyên môn vững vàng, một thái độ ân cần, một trái tim ấm áp, những lời nói nhỏ nhẹ cũng góp phần rất lớn trong việc điều trị và chăm sóc sức khoẻ bệnh nhân.
- Nguyễn Thanh OánhXem thêmBook
Với hơn 25 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Gây mê hồi sức, Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ CKII Nguyễn Thanh Oánh hiện đang giữ vai trò bác sĩ Gây mê hồi sức tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH). Bác sĩ Oánh không ngừng học hỏi, nâng cao tay nghề chuyên môn với các chứng chỉ đào tạo liên tục trong nước và quốc tế. Trước đây, bác sĩ Nguyễn Thanh Oánh đã từng có thời gian giữ nhiều chức vụ quan trọng như Phó Trưởng Khoa, Điều hành khoa Gây mê hồi sức tại Bệnh viện Nguyễn Trãi.
- Nguyễn Trường GiangXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Nguyễn Trường Giang có gần 10 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Nhi - Sơ sinh, chuyên sâu về điều trị và nuôi sưỡng trẻ sanh non, cực nhẹ cân và bệnh não thiếu oxy thiếu máu cục bộ. Bác sĩ Giang cũng giành được nhiều giải thưởng tại các hội nghị lớn và được huấn luyện chuyên sâu về Nhi Khoa tại Đại học Y Dược, Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh và hoàn thành nhiều khóa đào tạo tại Bệnh viện Nhi Đồng 2. Bác sĩ Nguyễn Trường Giang hiện đang công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Nguyễn Văn Cương
- Dương Thùy TrangXem thêmBook
ThS. BS. Dương Thuỳ Trang với 5 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Sản phụ khoa, được đào tạo chuyên môn bác sĩ đa khoa và Thạc sĩ Sản phụ khoa tại Đại Học Y Dược Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh. Không ngừng nâng cao chuyên môn, ThS. BS. Dương Thuỳ Trang đã tham gia nhiều khóa học, tập huấn về chuyên ngành sản phụ khoa. Bác sĩ Trang có nhiều năm công tác tại bệnh viện ĐKQT Phương Châu và hiện đang công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Lê Phạm Anh VyXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Lê Phạm Anh Vy tốt nghiệp bác sĩ CKI tại Trường Đại học Y khoa Phạm Ngọc Thạch . Nhằm nâng cao kiến thức và kỹ năng về chăm sóc sức khỏe ở lĩnh vực Dinh dưỡng, bác sĩ Anh Vy đã đạt được nhiều chứng chỉ về dinh dưỡng trong nước và quốc tế. Với kinh nghiệm 5 năm làm việc tại Bệnh viện Nhi Đồng Thành phố với vị trí bác sĩ Nhi - Dinh dưỡng, hiện nay bác sĩ Anh Vy đang giữ vị trí Trưởng khoa Dinh dưỡng - Tiết chế tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Phạm Thị Thanh Thảo
- Mai Viễn Phương
- Nguyễn Đức TrìnhXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Nguyễn Đức Trình là chuyên gia có hơn 10 năm kinh nghiệm lâm sàng trong lĩnh vực Răng Hàm Mặt, hiện đang công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH) và Phòng khám Nha khoa Quốc tế Kaiyen. Với nền tảng đào tạo bài bản và liên tục cập nhật các kỹ thuật tiên tiến thông qua nhiều khóa đào tạo chuyên sâu về cấy ghép implant và chỉnh hình răng mặt, bác sĩ Trình đã xây dựng được chuyên môn vững vàng cùng phong cách làm việc chuyên nghiệp. Những kinh nghiệm thực tiễn phong phú cùng sự am hiểu sâu sắc về các phương pháp điều trị hiện đại giúp bác sĩ đưa ra những giải pháp tối ưu, đảm bảo tính an toàn và hiệu quả cao cho từng trường hợp bệnh nhân.
- Võ Thái ChâuXem thêmBook
Bác sĩ Võ Thái Châu là chuyên gia Răng Hàm Mặt với 3 năm kinh nghiệm, tốt nghiệp Đại học Y Dược TP.HCM. Hiện đang công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH) và Phòng khám Nha khoa Kaiyen. Với tinh thần không ngừng nâng cao chuyên môn về cấy ghép implant, phục hình răng và veneer, bác sĩ cam kết mang lại những giải pháp nha khoa tối ưu - an toàn, hiệu quả và thẩm mỹ vượt trội cho bệnh nhân.
- Nguyễn Quang DiễnXem thêmBook
Với hơn 20 năm kinh nghiệm, BSCKI Quang Diễn đã có nhiều năm cống hiến với vai trò bác sĩ Gây mê tại bệnh viện Phú Nhuận và bác sĩ Cấp cứu & Hồi sức tại bệnh viện FV. Đặc biệt hơn, bác sĩ đã có hơn 1 năm gắn bó với Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ với vị trí Phó khoa Cấp cứu và Hồi sức vào năm 2018 - 2019.
- Trần Thanh PhongXem thêmBook
Với hơn 20 năm kinh nghiệm trong lĩnh vực Răng Hàm Mặt, bác sĩ Trần Thanh Phong liên tục trau dồi chuyên môn qua các khóa đào tạo chuyên sâu, bao gồm cấy ghép nha khoa và phục hình răng tại Đại học Loma Linda (Mỹ) năm 2011, cùng nhiều chứng chỉ chuyên gia lâm sàng và phẫu thuật Implant xương gò má. Bác từng công tác tại Bệnh viện Đa khoa Vạn Hạnh, Phòng khám Nha khoa Quốc tế Kaiyen và hiện là Bác sĩ Răng Hàm Mặt tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH).
- Nguyễn Công DũngXem thêmBook
Với gần 10 năm kinh nghiệm cùng nền tảng chuyên khoa Chấn thương Chỉnh hình, Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Công Dũng sở hữu lợi thế đặc biệt trong lĩnh vực Phẫu thuật Tạo hình – Thẩm mỹ, luôn chú trọng sự hài hòa giữa yếu tố chức năng và thẩm mỹ trong từng ca phẫu thuật. Đồng thời, Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Công Dũng ưu tiên ứng dụng nhiều kỹ thuật thẩm mỹ ít xâm lấn hiện đại, giúp đạt hiệu quả tối ưu, giảm đau, hạn chế sẹo và mang lại kết quả thẩm mỹ cao cho bệnh nhân và khách hàng. Trước khi công tác tại Bệnh viện Quốc tế Mỹ (AIH), Bác sĩ CKI Nguyễn Công Dũng đã có nhiều năm kinh nghiệm trong phẫu thuật Chấn thương Chỉnh hình và Tạo hình Thẩm mỹ tại các bệnh viện lớn như: Bệnh viện Nhi Đồng 1, Đại học Y Dược TP.HCM, Bệnh viện Hoàn Mỹ Sài Gòn và Bệnh viện Quốc tế Hạnh Phúc...
OCCUPYING 1/5 OF UROLOGICAL CASES: WHAT IS BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH)?

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is the most common benign condition in older men. When the prostate gland enlarges, it can compress the urethra, leading to lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). By age 55, approximately 25% of men experience symptoms; the frequency increases to about 50% in men aged 75, and 20–30% of them develop symptoms severe enough to require treatment.
Classification / Pathophysiology
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is not merely cellular hyperplasia. It is a complex histological process involving the proliferation of both glandular and stromal components, sometimes accompanied by small foci of atrophy. This enlargement is primarily due to a decrease in cell death rather than a rapid increase in cell proliferation. It is associated with increased sensitivity to androgens (such as dihydrotestosterone) and estrogens, as well as the promotion of stromal and collagen development.
Causes and risk factors
Age is the primary risk factor; the incidence of BPH significantly increases after the age of 40, with rates of 8%, 50%, 80% at ages 40, 60, and 90, respectively.
Factors: metabolic syndrome, chronic inflammation, family history, obesity, type 2 diabetes, physical inactivity, and erectile dysfunction are all identified as being associated with an increased risk of BPH.

Symptoms
Common symptoms include frequent urination, nocturia, incomplete bladder emptying, weak or interrupted urine stream, difficulty initiating urination, or urinary urgency. In severe cases, recurrent urinary tract infections, acute urinary retention, bladder stones, and secondary kidney failure due to collection of urine may occur.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of BPH is based on:
Medical history and thorough clinical examination, focusing on urinary symptoms and identifying other causes.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) to assess the size and texture of the prostate gland.
Urinalysis and additional tests if necessary: PSA, creatinine, ultrasound, measurement of post-void residual urine, cystoscopy, and urodynamic studies…
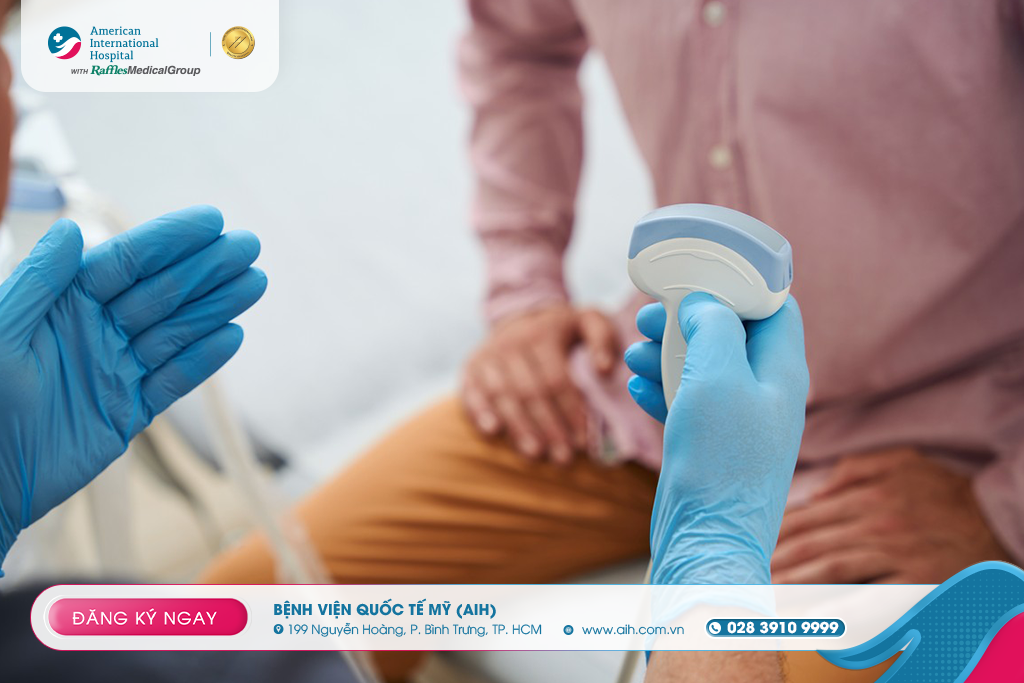
Treatment
a) Monitoring and Observation
For cases with mild symptoms, only watchful waiting. Treatment only begins if symptoms worsen.
b) Medical Treatment
Alpha-blockers: help relax smooth muscles in the bladder neck and gland, improving urine flow (e.g., tamsulosin).
5-alpha-reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs): limit DHT conversion, helping to reduce prostate volume over time.
Combining medications (e.g., tamsulosin + dutasteride) is more effective than monotherapy.
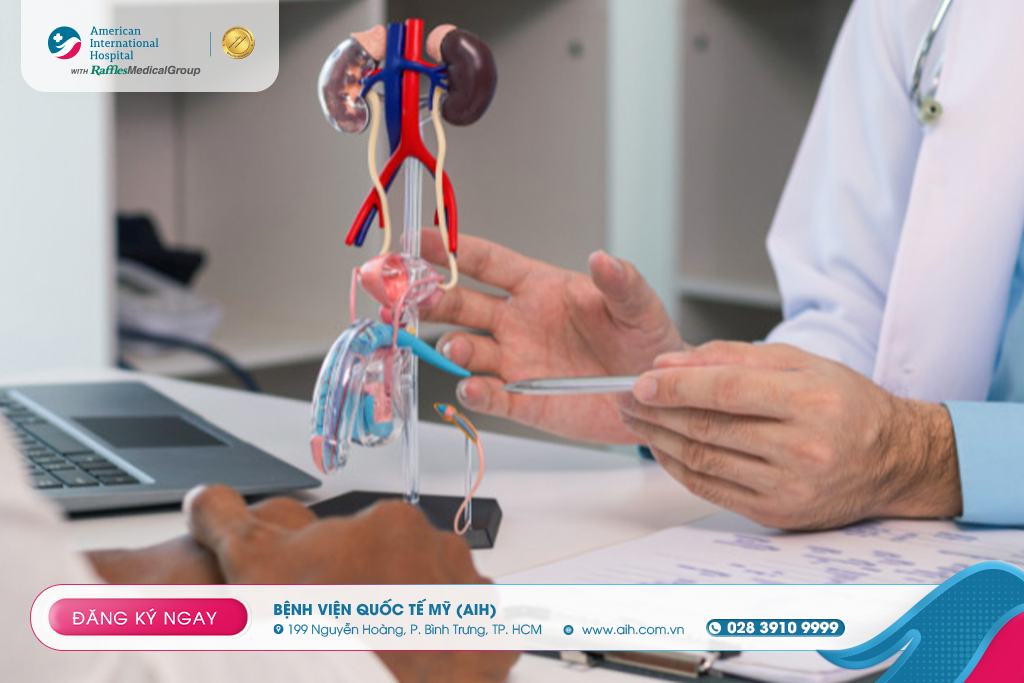
c) Surgical and minimally invasive procedures
TURP (Transurethral resection of the prostate): Transurethral endoscopic surgery is considered the gold standard.
HoLEP (Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate): uses a Holmium laser to remove internal glandular tissue, reducing obstruction.
Aquablation, Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL): minimally invasive endoscopic procedure to lift the urethra or reduce obstructive lesions.
PAE (Prostatic Artery Embolization): endovascular intervention that blocks blood flow to the gland to shrink its size and reduce symptoms; it is a new method with potential short-term equivalence to TURP.
WVTT (Water Vapor Thermal Therapy / Prostate Steam Treatment – Rezum): uses water vapor to destroy glandular tissue, is minimally invasive, and offers rapid recovery.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in middle-aged and older men, causing urinary disorders and significantly impacting quality of life. Accurate diagnosis relies on symptoms, clinical examination, and supportive laboratory tests. Treatment must be personalized: from watchful waiting, medication to minimally invasive procedures or surgery. Advances such as HoLEP, PAE, and Rezum offer new prospects in optimizing treatment, reducing side effects, and enhancing efficacy.

At the Department of Nephrourology - Andrology, AIH, patients will receive comprehensive and personalized care for each case from highly experienced urologists. Along with the support of modern diagnostic facilities, doctors can accurately diagnose complex diseases right from the first examination, leading to the highest possibility of successful treatment.
AIH is currently applying various treatment methods, from medication to minimally invasive surgeries such as endourology, keyhole surgery, etc., with the goal of bringing comfort and the fastest recovery to patients.
To receive consultation and schedule an appointment with specialists in Nephrourology - Andrology, please contact Hotline (028) 3910 9999 or INBOX Fanpage https://m.me/aih.com.vn.
References:
Singapore Urological Association
- bởi Admin AIH
- Danh mục: News & Events
Tìm kiếm
Tin tức
Bác sĩ




































































Để lại bình luận