Thông báo
Vui lòng điền vào thông tin bên dưới
Khẩn cấp
GASTROINTESTINAL CANCER: SYMPTOMS, CAUSES, AND EFFECTIVE PREVENTION
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer refers to a group of malignant diseases that include cancers of the stomach, esophagus, colon and rectum, liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts. This is one of the most common types of cancer with a high mortality rate if not detected and treated promptly. Understanding its symptoms, causes, prevention strategies, and modern treatment methods is key to protecting your health and that of your loved ones.
Common symptoms
Gastrointestinal cancer often develops silently, especially in the early stages. However, you should pay attention to the following warning signs:
1. Persistent digestive disorders
Bloating, indigestion, acid reflux, or a burning sensation in the stomach.
Commonly seen in patients with stomach or esophageal cancer.
2. Changes in bowel habits
Prolonged constipation or diarrhea, blood in stool or abnormal color.
A typical warning sign of colorectal cancer.
3. Unexplained weight loss
Rapid weight loss without dieting or doing physical activities.
4. Abdominal pain or discomfort
May be accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
Often associated with stomach, liver, or gallbladder cancer.
5. Fatigue, anemia
Anemia caused by chronic blood loss or nutrient deficiency from digestive tract.

Main causes of gastrointestinal cancer
Gastrointestinal cancer can result from a variety of factors:
1. Genetic and familial factors
Family history of gastrointestinal cancers (colorectal, gastric, esophageal cancer).
Inherited syndromes such as HNPCC (Lynch syndrome), FAP.
2. Dietary habits and lifestyle
High consumption of processed foods, red meat, fried foods.
Low intake of fiber, vegetables, and fruits.
Smoking and alcohol consumption.
3. Infections and bacteria
Helicobacter pylori: A major cause of chronic ulcerative gastritis.
Hepatitis B or C: Increasing the risk of liver cancer.
4. Chronic gastrointestinal diseases
Colon polyps could progress to cancer.
Chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease.
5. Age and gender
Age over 50: Cancer risk increases with age.
Gender: Certain cancers, such as esophageal cancer, are more common in men.

Treatment methods for gastrointestinal cancer
These days, various advanced treatment methods are available for gastrointestinal cancers, from minimally invasive surgery to targeted therapy and immunotherapy, helping improve treatment outcomes, reduce side effects, and enhance patients’ quality of life.
1. Laparoscopic and robotic surgery
Principle: Instead of traditional open surgery, laparoscopic and robotic techniques use small incisions to insert instruments and a camera into the body, allowing surgeons to observe and operate with precision.
Advantages:
Minimally invasive: Less damage to surrounding tissues, reducing postoperative pain.
Faster recovery: Patients can walk earlier, shortening the hospital stays.
Lower complication risks: Reduced bleeding, infection, and scarring after surgery.
Applications: Commonly used for cancers of the stomach, colon, rectum, esophagus, liver, and gallbladder.
2. Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and proton therapy
Chemotherapy: Uses anti-cancer drugs delivered through the bloodstream to destroy cancer cells throughout the body.
Radiotherapy: Employs high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells in localized areas.
Proton Therapy: An advanced form of radiation therapy that uses protons instead of X-rays, helping:
Destroy cancer cells with exceptional accuracy.
Protect healthy tissue, minimize side effects compared to conventional radiotherapy.
Applications: Beneficial for hard-to-reach tumors, advanced cancers, or cases where standard chemotherapy or radiotherapy is ineffective.
3. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy
Immunotherapy: Stimulates the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Targeted therapy: Uses specific drugs or molecules designed to target unique abnormalities of cancer cells, minimizing damage to normal cells.
Advantages:
Suitable for advanced or recurrent cancers.
Causes fewer systemic side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
4. Research and clinical trials
Objective: To develop new treatments that improve efficacy and reduce side effects.
Activities: Include testing new drugs, combining different therapies, and studying the molecular biology of tumors.
Benefits for patients:
Access to the most advanced treatment technologies.
Offers new opportunities for treating difficult or recurrent cancer cases.
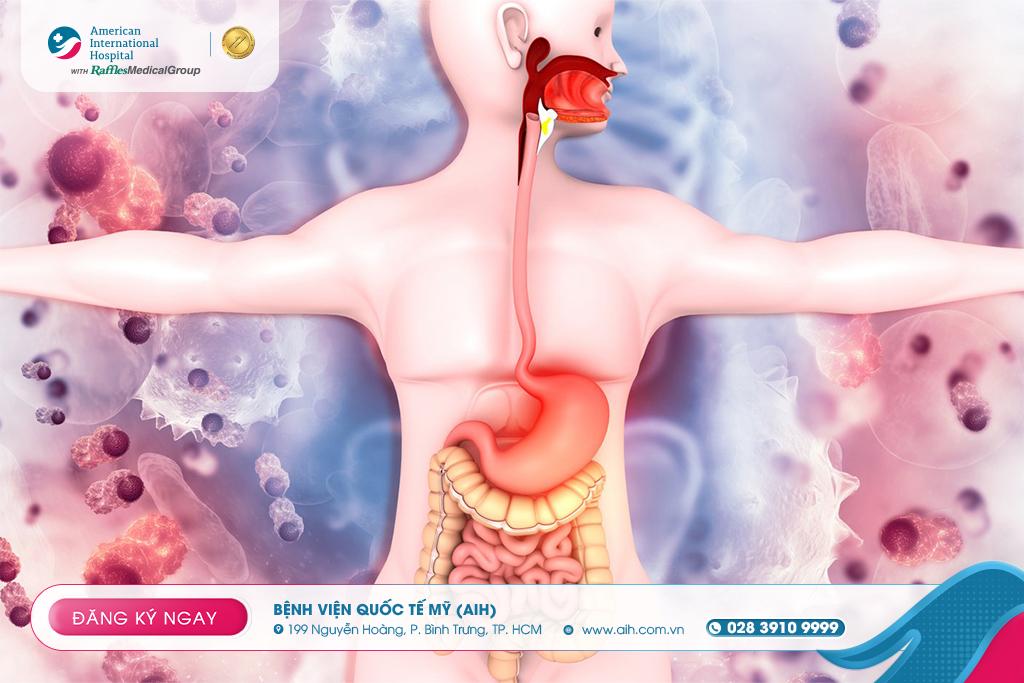
Preventing gastrointestinal cancer
Early prevention combined with lifestyle modifications is key to reducing the risk of gastrointestinal cancer. Below are effective methods you should incorporate:
1. Maintain a healthy diet
Eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains: These provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals that protect the digestive lining and strengthen the immune system.
Limit salty foods, red meat, and processed foods: Helps lower the risk of colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, and other chronic digestive diseases.
2. Exercise regularly
Engage in at least 30 minutes of physical activity daily: Maintains a healthy weight, supports digestion, and reduces the risk of chronic inflammation and cancer.
Activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, or yoga are all beneficial for digestive health.
3. Avoid alcohol and tobacco
Smoking and alcohol consumption significantly increase the risk of esophageal, stomach, and liver cancer.
Reducing or quitting these habits protects the cells of digestive tract lining and supports liver function.
4. Undergo regular screenings
Colonoscopy: Recommended starting at age 45–50, or earlier if you have a family history of colorectal cancer.
Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT): Detects early-stage colorectal cancer, even before symptoms appear.
Liver enzyme tests, ultrasound, or advanced tests: Advised for individuals at high risk of liver or gallbladder problems, helping detect abnormalities before they progress to cancer.
5. Manage stress and get enough sleep
Maintaining a relaxed mind, reducing stress, and getting 7–8 hours of sleep each night help the immune system function effectively, which could in turn strengthen the body’s natural defense against cancer.
6. Get vaccinated against cancer-related viruses
Hepatitis B vaccine: Prevents liver cancer caused by the hepatitis B virus.
Staying up to date with vaccinations significantly reduces the risk of liver cancer, especially in high-risk individuals.

Preventing gastrointestinal cancer is not only about early detection but also about maintaining a healthy lifestyle and daily habits. By adopting a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding alcohol and tobacco, undergoing periodic screenings, and getting vaccinated, you and your family can effectively reduce risks and move toward a healthier future.
Reference:
--------------------
Tìm kiếm
Tin tức
Bác sĩ





































































Để lại bình luận