Notification
Please fill in the information below
Urgent
GONARTHROSIS: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSIS
Although age is one of the main causes of gonarthrosis, there is currently a trend towards younger individuals experiencing gonarthrosis. Several factors such as genetics, injuries, or being overweight… also influence and accelerate the degeneration process. Below are some questions and detailed answers regarding issues related to gonarthrosis, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Osteoarthritis, commonly referred to as degenerative arthritis, is a condition in which the natural cushioning between the joints – cartilage – wears away. When this occurs, the ends of the bones in the joint rub together, reducing the shock-absorbing function of the cartilage. This friction causes inflammation and leads to symptoms such as pain, swelling, stiffness in the joints, decreased mobility, and sometimes the formation of bone spurs. 
Osteoarthritis is quite common nowadays, and the condition typically appears after the age of 40. Women tend to experience osteoarthritis more frequently than men.
► Causes of osteoarthritis
Age: In older individuals, the ability of cartilage to recover decreases.
Weight: Increased weight puts pressure on all joints, especially the knee joint. For every 0.45 kg increase in weight, there is a corresponding increase of 1.35 to 1.8 kg in weight on the knee.
Genetics: This includes genetic mutations that may make a person more susceptible to gonarthrosis. It can also be due to congenital deformities in the shape and structure of the bones surrounding the knee joint.
Gender: Women aged 55 and older are more likely to develop gonarthrosis than men.
Repetitive stress injuries: Individuals whose jobs involve many activities that can stress the joints, such as kneeling, squatting, or lifting heavy objects, are more likely to develop gonarthrosis due to continuous pressure on the joints.
Sports: Athletes participating in sports like football, tennis, or long-distance running may have a higher risk of developing gonarthrosis. However, it is important to note that moderate exercise performed regularly strengthens the joints and can reduce the risk of osteoarthritis. Additionally, weak muscles around the knee joint can lead to osteoarthritis.
Other diseases: People with rheumatoid arthritis, the second most common type of arthritis, certain metabolic disorders such as iron overload or excessive growth hormone, also have a higher risk of developing osteoarthritis.

Gonarthrosis is trending to become more common among younger people
► Symptoms of gonarthrosis
The symptoms of gonarthrosis may include:
Pain that increases with activity but decreases somewhat with rest
Swelling
Stiffness in the knee, especially in the morning or after sitting for a while
Reduced range of motion in the knee, making it difficult to get in and out of chairs or vehicles, use stairs, or walk
A popping or crackling sound heard when the knee moves.
► Complications of gonarthrosis
The complications related to non-surgical treatment are primarily associated with the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Common side effects of NSAID use:
Abdominal pain and heartburn
Gastric ulcers
Tendency to bleed, especially when using aspirin
Kidney problems
Common side effects of intra-articular corticosteroid injection:
Pain and swelling (cortisone flare)
Skin discoloration at the injection site
Hyperglycemia
Infection
Allergic reaction
Common side effects of intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection:
Pain at the injection site
Muscle pain
Difficulty walking
Fever
Chills
Headache
Complications related to high tibial osteotomy (HTO):
Recurrence of deformity
Loss of posterior slope of the tibia
Patella baja (low-lying patella)
Compartment syndrome
Peroneal nerve palsy
Infection
Persistent pain
Thrombosis
Complications related to Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty (UKA):
Stress fracture of the tibia (stress fracture)
Subsidence of the tibial joint surface
Infection
Osteolysis
Persistent pain
Neurovascular damage
Thrombosis
Complications related to Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) :
Infection
Instability (joint laxity)
Osteolysis
Neurovascular damage
Fracture
Patellar malalignment
Patellar clunk syndrome
Joint stiffness
Peroneal nerve palsy
Wound complications
Heterotopic ossification
Thrombosis
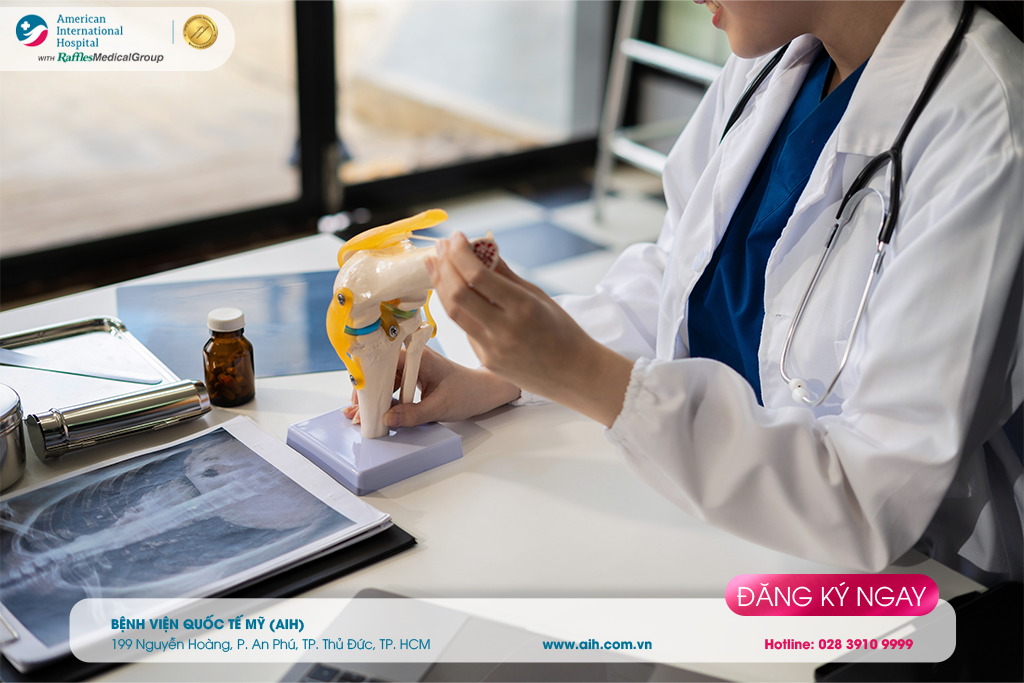

► How is gonarthrosis diagnosed?
The diagnosis of gonarthrosis is based on clinical symptoms and imaging diagnostics, including:
Radiography, which can reveal bone and cartilage damage as well as the presence of bone spurs.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): this can be performed to detect other associated injuries such as cartilage, joint and ligament issues....
The doctor can use blood tests to rule out other conditions that may cause pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis, another type of arthritis caused by an autoimmune disorder.
The main goal of treating gonarthrosis is to reduce pain and help you move more easily. The treatment plan typically includes a combination of the following measures:
Weight Loss: Losing even a small amount of weight, if necessary, can significantly reduce knee joint pain caused by gonarthrosis.
Exercise: Strengthening the muscles around the knee joint helps stabilize the joint and reduce pain. Stretching exercises help keep the knee joint mobile and flexible.
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatories: This includes over-the-counter options such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen sodium. Do not self-medicate with over-the-counter drugs for more than 10 days without consulting a doctor, as this may increase the risk of side effects. If over-the-counter medications do not relieve pain, your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatories or other drugs to help alleviate pain.
Corticosteroid or Hyaluronic Acid injections into the knee joint: Steroids are powerful anti-inflammatories. Hyaluronic acid is often present in joints as a type of lubricant.
Alternative therapies: Some alternative therapies that may be effective include topical creams containing capsaicin; acupuncture; or supplements, including glucosamine and chondroitin or SAMe.
Use of devices such as braces: There are two types of braces: unloader braces that help reduce weight on the arthritic knee joint; and functional braces that provide support to the entire knee joint.
Physical therapy and psychological therapy: If you have difficulty with daily activities, physical therapy or psychological therapy can help improve symptoms. Physical therapists will guide you on how to strengthen muscles and make the joints more flexible. At the same time, psychological therapists will instruct you on how to perform normal daily activities that support pain relief.
Surgery: When other treatment measures are ineffective, knee arthroplasty is an optimal solution.
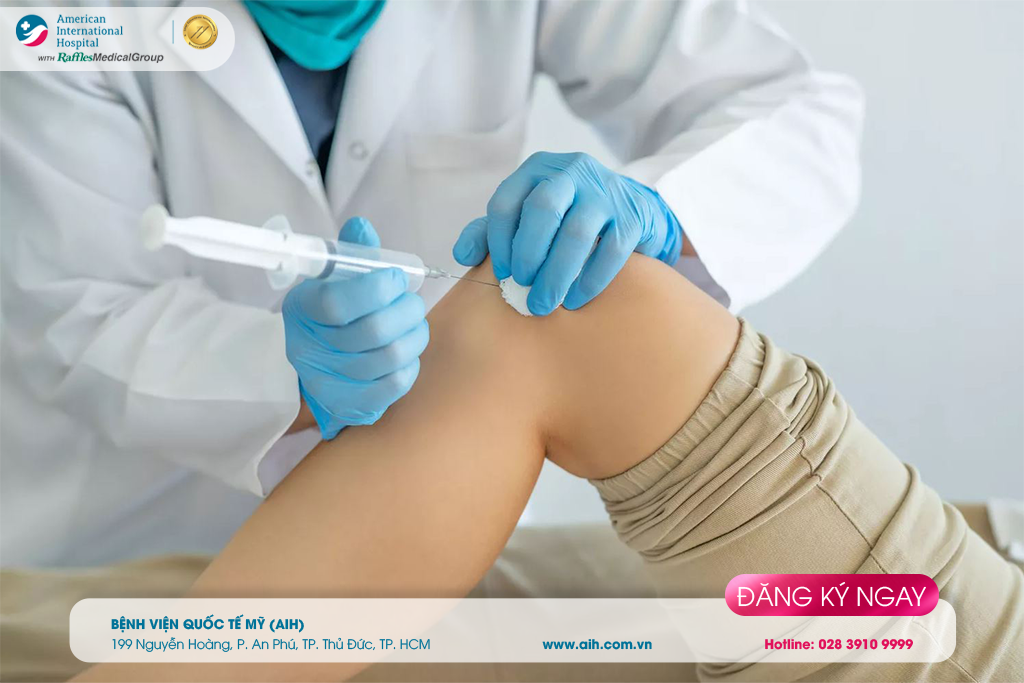
Injecting corticosteroids into the knee joint helps achieve significant effects
Post-operative care and recovery after knee arthroplasty aim to restore the highest possible level of mobility and complete control of the muscles around the operated knee. Full recovery is an crucial requirement for a successful surgery.
After knee arthroplasty, you will need to stay in the hospital for 1-2 days. During this time, a specialist will guide you through physical therapy exercises to help you recover the movement and function of your knee joint.
► Prevention of osteoarthritis
Avoid kneeling and squatting.
Maintain your ideal body weight.
Low-impact exercises can improve joint health, such as swimming, gentle walking appropriate to your health condition, and cycling.
For the elderly, it is advisable to avoid climbing stairs.
The symptoms of gonarthrosis often develop slowly and gradually increase over time.
You should consult a doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
Pain when walking or climbing stairs
Pain when lying down
Regular inflammation
Stiffness in joints after a period of inactivity
Knees becoming bent.
A grinding or popping sensation when moving the joint.

At the Orthopedic Department of American International Hospital (AIH), we provide various treatment solutions for musculoskeletal disorders: from diagnosis, conservative treatment, surgery, and rehabilitation.
--------------------




































































Leave a comment