Notification
Please fill in the information below
Urgent
SPINAL OSTEOARTHRITIS, CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
The spine plays a key role in supporting the body, protecting the nerves, and allowing us to move flexibly, while also helping to reduce pressure by bearing the weight of the body.
Spinal osteoarthritis is a chronic musculoskeletal condition that commonly occurs in middle age. However, in recent years, the disease has shown a trend towards affecting younger individuals and has resulted in many severe complications.
► What is spinal osteoarthritis?
Spinal osteoarthritis is a condition characterized by the deterioration of cartilage in the joints and discs in the neck and lower back. Sometimes, osteoarthritis leads to osteophytes that compress nerve roots. This can cause weakness and pain in the arms or legs.
► Who is at risk of developing spinal osteoarthritis?
Spinal osteoarthritis is a consequence of the natural aging process of the body, especially in old age. However, younger individuals can also suffer from this condition due to various other causes:
Has a history of spinal injury or damage
There is a history of genetic defects related to cartilage
For individuals under 45 years old, spinal osteoarthritis is more common in men. After the age of 45, spinal osteoarthritis is more common in women.
Spinal osteoarthritis also occurs more frequently in overweight individuals.
It also happens more often in those who have jobs or engage in sports that involve intense physical activity.

► Causes of spinal osteoarthritis
Spinal osteoarthritis often occurs due to damage and collapse of the vertebral body, in the cartilage layer of the joint surfaces.
The combination of muscle spasms and arthritis causes pain.The facet joints in the lower back are prone to degeneration due to cartilage damage. The impact of injuries over a long period can lead to weakening or degeneration of these joints.
Tears and fibrosis of the intervertebral discs are also causes of degeneration because the discs between the vertebrae serve to absorb shock, limit wear, and prevent collapse of the joint surfaces.
► The common symptoms of spinal osteoarthritis
Spinal osteoarthritis is most commonly seen in the cervical and lumbar regions. Degeneration of the thoracic spine is less common.
One of the common symptoms of the disease is stiffness or pain in the neck or back, which can cause weakness or numbness in the legs or arms if it is severe enough to affect the spinal nerves or spinal cord. Typically, discomfort in the back will decrease when the patient rests while lying down. As the disease progresses, patients may experience continuous pain. Patients feel a crunching sensation when moving their spine.
In addition to the physical effects, individuals with spinal osteoarthritis may also encounter social and emotional issues due to being prevented in daily activities, reduced work performance, which can lead to feelings of depression or helplessness.

► The effects of spinal osteoarthritis:
Spinal osteoarthritis can cause pain, functional impairment, and disability. Additionally, spinal osteoarthritis can lead to spinal stenosis, herniated discs, myelopathy, radiculopathy, spondyloarthritis, and spondylolisthesis.
Spinal stenosis can lead to two clinical syndromes, including cervical myelopathy and lumbar radiculopathy. Lumbar spinal stenosis may present as persistent or intermittent pain, weakness, and sensory symptoms in the dermatomes activated when standing or walking, and these symptoms decrease when sitting or lying down.
Herniated discs cause persistent lower back pain in 1-2% of the population aged 35 to 45 years.
Lumbarthrosis can lead to degenerative spondylolisthesis, most commonly occurring at L4 over L5, where the upper vertebra slips forward on the lower segment due to weak facet joints.
► How is spinal osteoarthritis diagnosed?
Doctors can rely on clinical symptoms and imaging from X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
Radiography: Check for bone lesions, bone spurs, collapse, slippage…
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Assessment of the condition of the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, and nerve roots.
Blood test to rule out other diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis and spinal tuberculosis…
Nutritional supplements
In addition, pain relievers can also be used to treat spinal osteoarthritis. Ointments and topical creams can also be used to treat pain. They are applied to the skin in the area of pain, but they are less effective.
Furthermore, joint injections (corticosteroids, platelet-rich plasma PRP…) also provide high treatment efficacy.
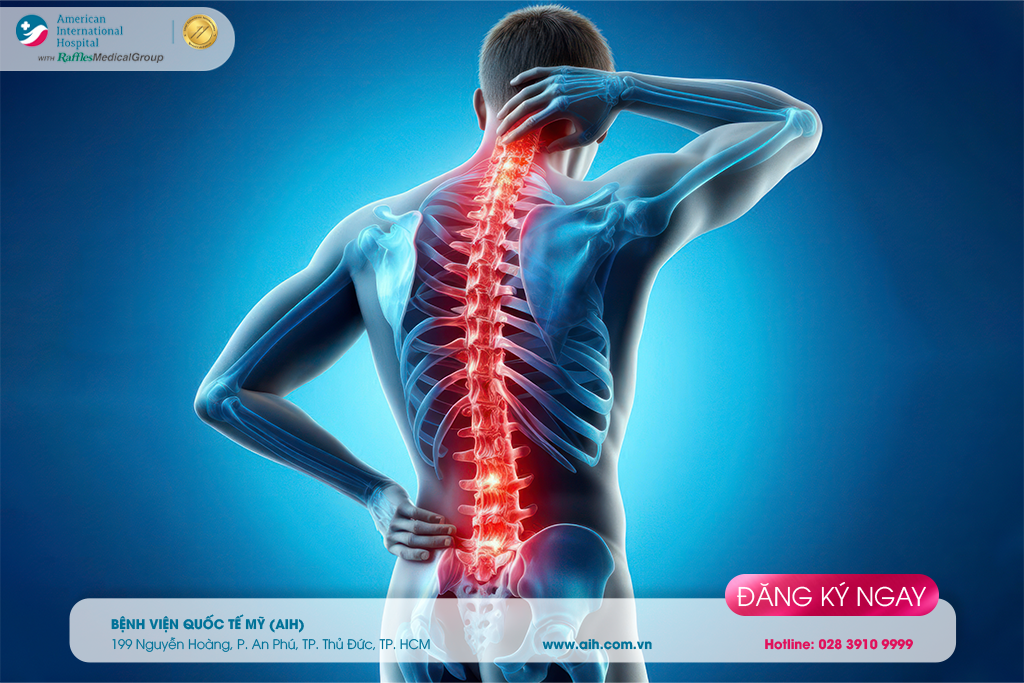
► When surgical treatment is necessary?
Most cases of spinal osteoarthritis can be treated without surgery, but surgery is sometimes performed and can be considered as a last treatment option. Surgery is recommended in cases where the patient does not respond to medical treatment; shows signs of nerve root or spinal cord compression; has signs of grade 3-4 vertebral slippage; or has severely damaged intervertebral discs…
► How to prevent spinal osteoarthritis?
Establish a positive lifestyle and a healthy diet that is rich in calcium.
Change poor postures in daily activities and limit activities that overload the spine.
Engage in low-impact exercises such as swimming, yoga, and cycling.
Avoid smoking and using tobacco products.
Wear appropriate protective gear for all work, sports, and hobbies.





































































Leave a comment