Thông báo
Vui lòng điền vào thông tin bên dưới
Khẩn cấp
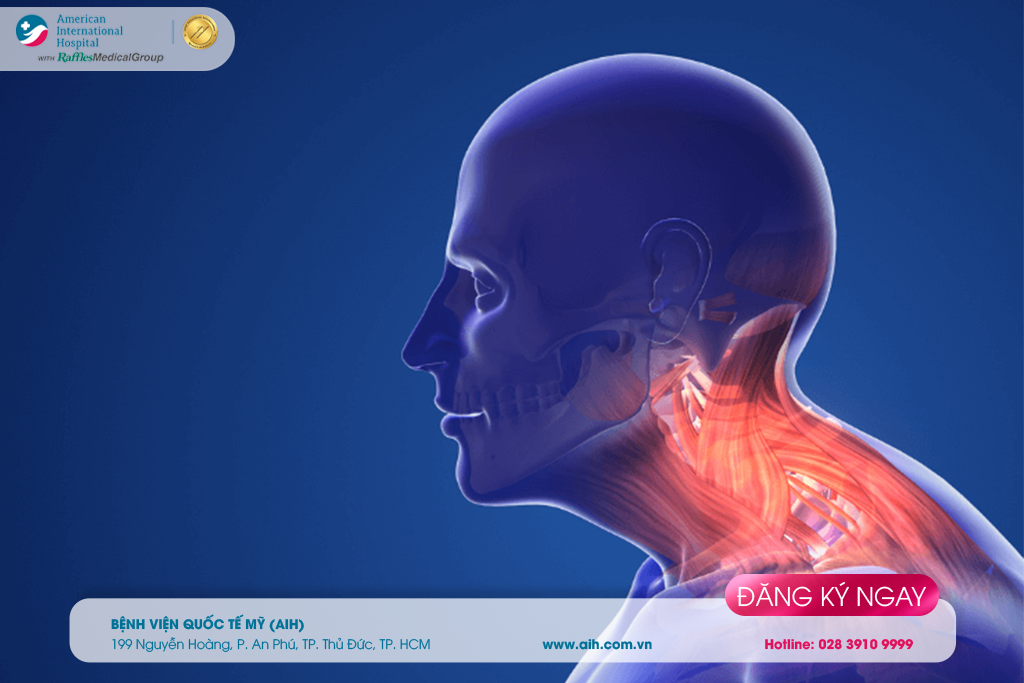
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS - CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
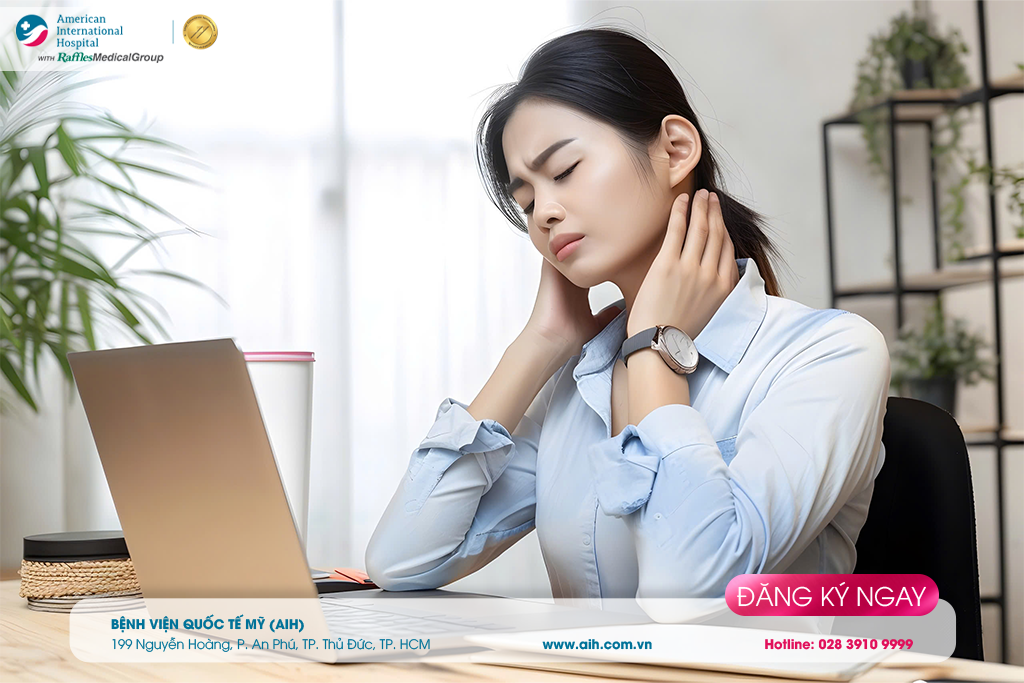
Cervical spondylosis is a term encompassing many progressive degenerative changes that affect all parts of the cervical spine, such as intervertebral discs, facet joints, Luschka joints, yellow ligaments, and bone fragments. The degenerative changes usually develop without any symptoms. It can manifest as cervical spine problems are neck and shoulder pain, stiff neck, or radicular symptoms if there is compression of the nervous structure, which can arise from many causes.
► Cervical spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis is more prevalent in the senior age group and above, and usually incidentally detected via X-ray results ordered when patients visit for neck pain and stiffness. Imaging findings can reveal subchondral bone sclerosis, articular surface depression, and bone spurs. These are associated with changes of the cervical bones, discs, and joints. Thickened bone and ligaments encroach on the spinal canal space.

► Several other causes of cervical spondylosis
There are some other possible causes of cervical spondylosis besides aging, including:
- Family history of cervical spondylosis: This condition can have genetic components.
- Neck trauma or injury: If you experienced neck injury in the past, your cervical discs and ligaments can be affected over time.
Occupation, lifestyle or hobbies: There are several jobs, hobbies or sports that require your neck to move in a repetitive way, or head to lift over an extended time. This can eventually strain the cervical discs and ligaments. - Smoking: There is a link between smoking and neck pain.
Depression: Research shows increased risks of cervical spondylosis in people with depression.
Incorrect movements: Improper postures such as excessive neck bending or lifting can cause damage to the cervical discs and ligaments over time.
Disc desiccation: When your cervical discs dehydrate over time, they shrink and are unable to cushion, leading to direct contact between bones.
Herniated discs: If a disc cracks, it can compress the spinal cord or nerve roots.
Bone spurs: Abnormal formations along the spine, known as bone spurs, can encroach the spinal canal or the foramina, where nerves exit, resulting in cervical spinal stenosis.
Fibrous ligaments: Ligaments are bands of tissues that help stabilize bones and joints in the correct position. They can become stiff overtime, causing difficulty moving or bending over.

► Common symptoms of cervical spondylosis
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Headache, possibly originating from the neck
- Pain in the shoulder or arm
- Inability to turn the head or bend the neck fully, sometimes interfering with driving
- Grinding sound while rotating the neck
- Some other less common symptoms include dizziness, headache, palpitation (fast, strong, or irregular heartbeat), vomiting, abdominal or digestive discomfort, ringing in the ears, blurred vision and impaired memories. Research also suggests that chronic neck pain due to cervical spondylosis is linked to hypertension.
These symptoms tend to improve with proper rest, and normally develop more in the morning and late in the day.

1. Symptoms of nerve root pain:
Cervical spondylosis can cause cervical radiculopathy (nerve root pain), when bone spurs compress nerve roots as they exit the spinal cord. The most common symptom is pain radiating down one or both arms. Putting a hand on the top of the head can help alleviate this. You can also notice other symptoms in the shoulders, arms, chest or upper back. It can worsen with neck movement, for example:
Pins-and-needles or tingling sensation in the fingers or hands
Muscle weakness
Loss of sensation
Weak reflexes
2. Symptoms of Cervical Myelopathy:
If cervical spondylosis applies pressure on the spinal cord (cervical spinal stenosis), it can lead to cervical myelopathy. Symptoms of cervical myelopathy due to spondylosis can include:
- Pricking sensation, numbness and/or weakness in the arms, hands, legs, or feet.
- Loss of coordination and difficulty walking
- Abnormal reflexes
- Muscle spasms
- Bladder and bowel dysfunction (Urinary incontinence)
3. Dizziness caused by cervical spondylosis
Although rare, some people with cervical spondylosis can experience dizziness. Symptoms of dizziness due to cervical spondylosis may include:
- Feeling like floating
- Light-headedness
- Unstable feeling or lack of coordination
- Postural changes
- Changes of vision, like rapid eye movements
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
4. Headache caused by cervical spondylosis
Individuals with cervical spondylosis, particularly when associated with arthritis, may experience headaches.
► Does cervical spondylosis affect the brain?
Cervical spondylosis can impact motor function, movement, cognitive skills and quality of life.
► Diagnosing cervical spondylosis
1. Clinical evaluation: The doctor can ask you several questions, for example:
- When did the pain start? How does it feel like? How long does it last?
- Does anything noticeably happen when the pain starts?
- Does anything relieve the pain or make it go away?
- Have you ever had neck injuries or experienced similar problems before?
The doctor may also examine your reflexes, muscle tone of the whole arm, sensation, motor function and observe your walking gait to detect if you have neurological abnormalities.
2. Neck X-Ray: Cervical X-Ray can identify abnormalities such as degeneration signs, bone spurs, or foraminal stenosis.
3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI provides specific changes within the vertebrae, including nerve compression.
4. Computerized Tomography (CT) scan with contrast: Offers detailed images of the spinal cord, spinal canal, as well as nerve roots.
5. Electromyography (EMG): Identifies peripheral nerve injuries or radiculopathy.
► Treatment of cervical spondylosis
1. Medical treatment: primarily aimed at treating symptoms, including:
- Resting
- Using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids
- Immobilization with a neck brace to limit neck movement
- Other physical therapy options, including warm or cold compress, stretching or therapeutic exercises.
- Nerve block injection to relieve neck pain.
2. Surgical treatment: This is indicated in case of herniated discs, spinal cord compression, nerve root compression, or instability of the spine.
3. Physical therapy: A physical therapist will demonstrate exercises that help strengthen neck, shoulder, and arm muscles. Techniques like massaging and stretching can effectively alleviate the pain for patients.

► Post-treatment tips for patients
Engaging in regular and frequent exercises can improve neck movement. If pain arises during practice, you need to seek medical attention immediately for proper guidance.
► Effective prevention of cervical spondylosis
The following methods can help prevent or slow the progression of cervical spondylosis:
Protect your neck: Practice neck-protecting exercises before physical activities. Avoid over-stretching the neck or moving the head abruptly. When doing activities that can potentially harm the neck, use proper equipment such as a neck brace.
Avoid excessive repetitive movements such as looking upward or reaching overhead.
Regularly exercise or do yoga poses tailored to treat cervical spondylosis to maintain joint and bone mobility.
--------------------
Tìm kiếm
Tin tức
Bác sĩ