Thông báo
Vui lòng điền vào thông tin bên dưới
Khẩn cấp
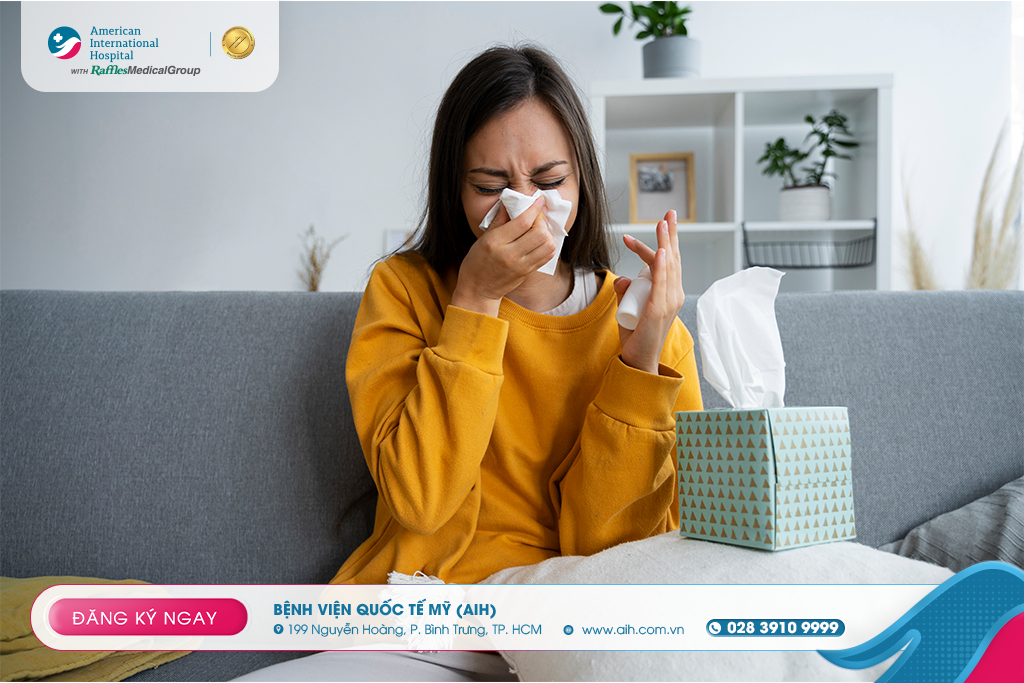
SINUSITIS: WHEN TO SEEK MEDICAL CARE AND SURGICAL INTERVENTION?
Sinusitis is an inflammation or infection of the lining of the paranasal sinuses – the air-filled cavities surrounding the nose and face – leading to mucosal swelling, increased mucus production, and blockage of sinus drainage pathways.
The condition often develops after a cold or allergic rhinitis, leading to nasopharyngitis and blocking sinus pathways, creating favourable conditions for viruses or bacteria to grow. Sinusitis can be short-term or long-lasting; if not properly managed, it may recur frequently or progress to chronic sinusitis.
Classification
Acute sinusitis: Sudden onset with distinct symptoms, usually resolved with appropriate treatment.
Subacute sinusitis: Symptoms persist longer than acute sinusitis but have not yet become chronic.
Chronic sinusitis: Prolonged or recurrent inflammation, often associated with underlying conditions.
Recurrent sinusitis: The patient experiences multiple acute episodes in a year (usually ≥3) with symptom-free intervals in between.

Causes
The causes of sinusitis include:
1. Respiratory viruses & post–common cold infections
Virus-caused inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa, blocking the sinus openings.
Allergies may also trigger nasal inflammation and edema, leading to sinus obstruction.
2. Constitutional and structural factors
Deviated nasal septum: blocks sinus drainage pathways.
Nasal polyps: Soft tissue growths within the sinuses or nasal cavities that obstruct mucus flow.
Enlarged adenoids (in children): May block sinus drainage routes.
3. Systemic diseases and immune-related factors
Allergic rhinitis often coexists with sinus inflammation.
Immune disorders such as HIV, cystic fibrosis, or other immunodeficiency states can make sinusitis persistent or recurrent.
4. Environmental and external factors
Passive smoking, dust exposure, and air pollution irritate the mucosa and increase the risk of chronic sinusitis.
Humid climate, temperature changes, or frequent water exposure (e.g., swimming) may affect respiratory function and sinus ventilation.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of sinusitis vary depending on the type, age, and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
Nasal congestion or blockage, difficulty breathing through the nose.
Runny nose (may be clear or thick yellow/green) or post-nasal drip.
Facial pain or pressure: around the eyes, forehead, or cheeks; often worse in the morning or when bending forward.
Reduced or lost sense of smell, sometimes accompanied by decreased taste.
Cough, especially at night or when lying down; may be associated with a sore throat or bad breath.
Fever, which may or may not be present (more common in acute or severe cases).
Persistent or recurrent symptoms: fatigue and decreased quality of life.

Diagnosis
The diagnosis of sinusitis typically includes:
1. Medical history
Duration of symptoms (acute, chronic,recurrent).
Suggestive symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain, nasal discharge, reduced sense of smell, or post-nasal drip.
Risk factors (allergies, polyps, structural abnormalities, environmental factors).
2. Specialist examination
Nasoendoscopy to visualize the nasal mucosa, polyps, obstructions, and presence of mucus in or around the sinus openings.
Facial palpation to check for tenderness or swelling over the cheeks, forehead, or eyes, which may indicate sinus inflammation.
3. Imaging studies
CT scan (sinus CT): Performed when structural obstruction (such as polyps, deviated septum, tumors) is suspected, or when medical treatment fails.
MRI: Rarely used, except when there is suspicion of abnormal masses or spread beyond the sinuses.
4. Supporting tests
Allergy testing (skin or serum tests) when allergy is suspected as a contributing factor.
Nasal secretion culture may be performed in severe or treatment-resistant cases to identify bacterial causes.
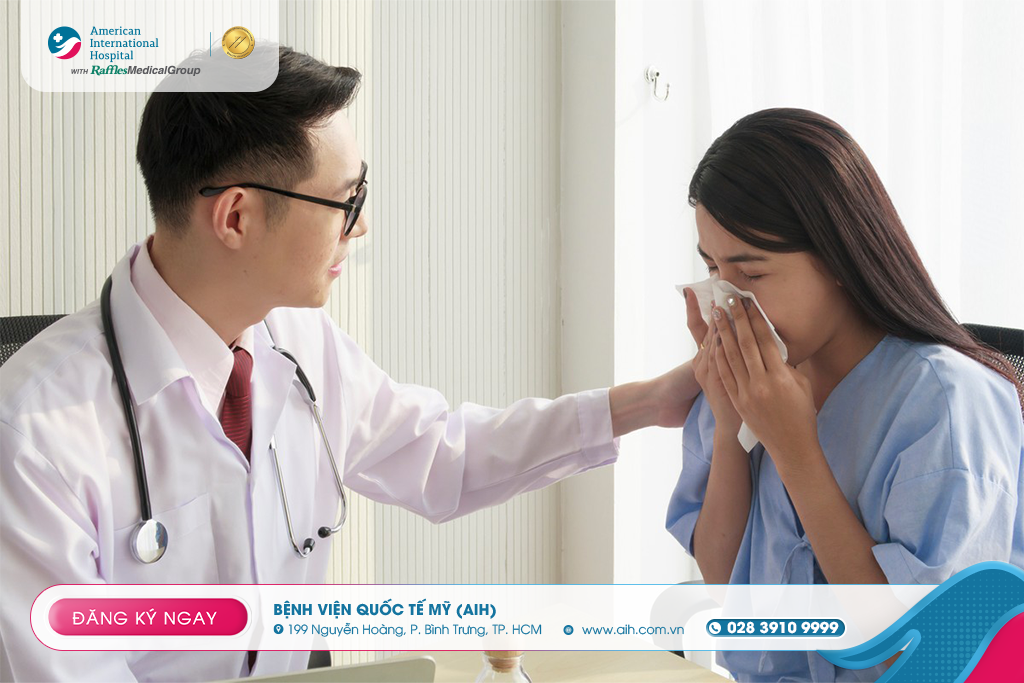

Treatment
The management of sinusitis depends on its severity (acute, chronic), causes, and the impact on the patient’s quality of life. The main approaches include:
1. Non-drug / Home supportive measures
Steam inhalation or saline nasal irrigation to thin mucus and promote sinus drainage.
Increase fluid intake, get adequate rest, and maintain a clean-living environment; avoid tobacco smoke and irritants.
Use pain relievers / nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and reduce mucosal swelling.
2. Prescription medications
Intranasal corticosteroid sprays to reduce local inflammation, especially in chronic sinusitis or when nasal polyps are present.
Antibiotics may be prescribed for severe symptoms, fever, facial pain, or when acute bacterial sinusitis is suspected, or if symptoms do not improve after initial therapy. Antihistamines may be used if allergic rhinitis is present.
Oral corticosteroids may be considered in severe chronic cases or with large polyps when nasal sprays are insufficient.
3. Surgical / specialist interventions
For large polyps, structural abnormalities (such as deviated septum), or sinus blockage significantly affecting quality of life, Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (ESS) may be performed to remove obstructions and improve sinus drainage.
Septoplasty may be indicated if a deviated septum is contributing to sinus obstruction.
4. Follow-up and prevention of recurrence
Monitor treatment response: if there is no improvement after an appropriate period → re-evaluate the diagnosis, adjust medication, or refer to a specialist.
Treat underlying allergies to reduce recurrence risk.
Avoid environmental irritants such as pollution, cigarette smoke, and allergens; maintain proper humidity in the living environment.
--------------------
Tìm kiếm
Tin tức
Bác sĩ





































































Để lại bình luận