Notification
Please fill in the information below
Urgent
UNDERSTANDING ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION: FROM DIAGNOSIS TO MODERN TREATMENT METHODS
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection of the penis sufficient for satisfactory sexual activity. This condition is not only common in older individuals but can occur across all age groups, although the risk increases with age. According to a survey, the frequency of erectile dysfunction increases with age, and by 2025, it could affect approximately 322 million men globally.
Classification
ED can originate from two main groups of causes:
Organic causes: including vascular damage (such as atherosclerosis causing insufficient blood flow to the penis), neurological disorders, hormonal imbalance, or smooth muscle damage in the corpus cavernosum, leading to a reduced ability to maintain an erection.
Psychological causes: although previously often considered the primary reason, it is now viewed as a contributing factor, sometimes complicating the ED condition, especially when the patient experiences anxiety or psychological stress.
Causes – risk factors
Common causes include:
Vascular system diseases (hypertension, atherosclerosis, dyslipidemia)
Diabetes, neurological diseases
Hormonal imbalance (e.g., low testosterone)
Side effects of medications, alcoholism, cigarette
Peyronie's disease (causing penile deformity)

Factors that increase the risk of ED:
Older age, as it is asslociated with the accumulation of many chronic diseases.
Cardiovascular factors: hypertension, high LDL-cholesterol, atherosclerosis – factors that reduce blood flow to the penis.
Diabetes: causes microvascular and nerve damage, prevalent in up to 35–50% of patients, especially in the US.
Psychological factors: stress, depression, unstable relationships also contribute to ED.
Symptoms
Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection long enough for intercourse.
Reduced libido, sometimes accompanied by premature ejaculation.
Causes psychological stress, affecting mental well-being and sexual life, potentially leading to low self-esteem or reluctance to discuss with a doctor.

Diagnosis
The diagnostic process involves two main factors:
Clinical examination & medical history: including underlying conditions, treatments, psychological factors, as well as a general genital assessment.
Supportive tests: may include vascular ultrasound of the penis to assess blood flow, blood tests (to check for diabetes, cardiovascular issues, testosterone levels), urine tests, and psychological evaluation if necessary.
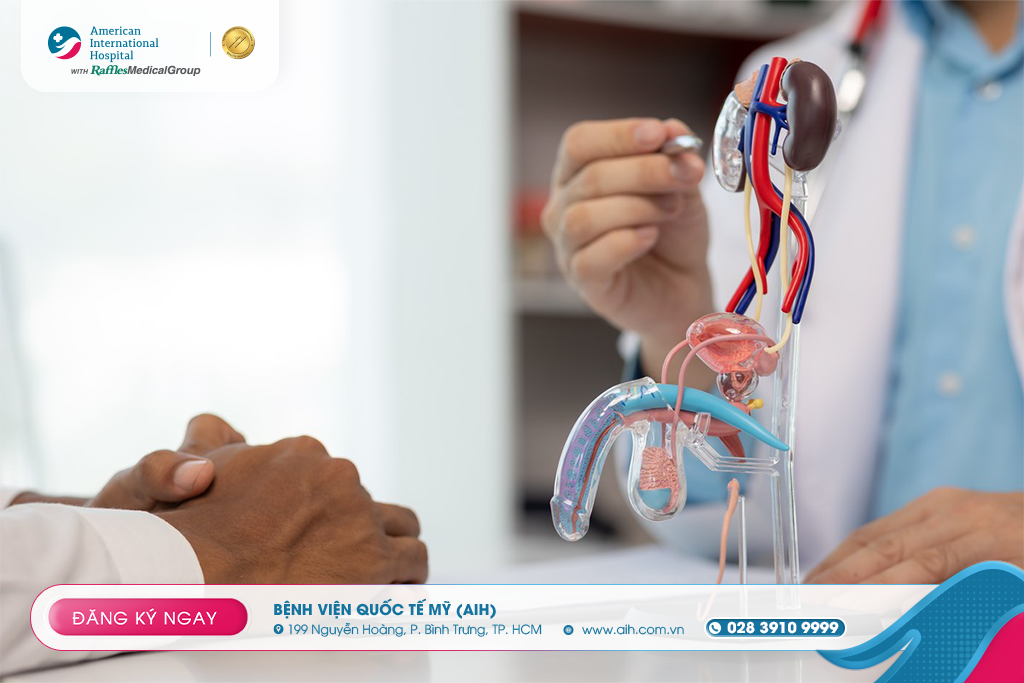
Treatment
Non-pharmacological treatments:
Increased physical activity (running, swimming, cycling) helps improve overall blood circulation and blood flow to the penis.
Oral medications:
PDE5 inhibitors such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), etc., help increase blood flow to the corpus cavernosum of the penis.
Injection therapy and assistive devices:
Intracavernosal injection: uses vasodilators like prostaglandin E1… to induce an erection, but may cause pain or tissue scarring.
Vacuum constriction device: creates an erection by drawing blood into the penis, then uses a constriction ring to maintain the erection. This method is safe, but can be inconvenient or uncomfortable.
Shock wave therapy (ESWT):
Low-intensity pulsed wave technology aims to stimulate angiogenesis in the corpus cavernosum, improving blood flow - non-invasive, typically tested in 6–12 sessions, each lasting 15–20 minutes.

Surgery & Device Implantation:
Penile prosthesis: This involves either semirigid or inflatable types, assisting effective erections for cases where medical treatments are unsuccessful. There is a high satisfaction rate, and risks such as infection or mechanical failure have decreased due to technical improvements.
Vascular surgery (arterial revascularization or ligation of venous leaks) is reserved for a small number of specific cases, such as acute vascular injury in young men.
Latest advancement
Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): a non-invasive method aimed at improving penile microvasculature and erectile blood flow, currently being implemented and evaluated.
Penile prosthesis with modern techniques, offering higher satisfaction rates and reduced complications compared to before.
Identifying ED as a warning sign for cardiovascular disease: research from Johns Hopkins indicates that ED can be an early sign, suggesting the need for thorough cardiovascular screening in men experiencing erectile dysfunction.

Erectile dysfunction is a common sexual dysfunction that can be related to many physical and psychological factors. Effective treatment requires a comprehensive evaluation, and the use of methods appropriate for each individual, from lifestyle changes, medication use, to minimally invasive interventions or implants when necessary. ED is also a warning sign of cardiovascular diseases – especially helping to detect serious cardiovascular risks early.
At the Department of Nephro-urology - Andrology, AIH, patients will receive comprehensive and personalized care for each case from highly experienced urologists. Along with the support of modern diagnostic facilities, doctors can accurately diagnose complex diseases right from the first examination, leading to the highest possibility of successful treatment.
AIH is currently applying various treatment methods, from medication to minimally invasive surgeries such as endourology, laparoscopic surgery, etc., with the goal of bringing comfort and the fastest recovery to patients.
To receive consultation and schedule an appointment with specialists in Nephro-urology - Andrology, please contact Hotline (028) 3910 9999 or INBOX Fanpage https://m.me/aih.com.vn.
References:
Hopkins Medicine
Raffles Medical Group
Search
Latest News
Our Doctor





































































Leave a comment