Notification
Please fill in the information below
Urgent
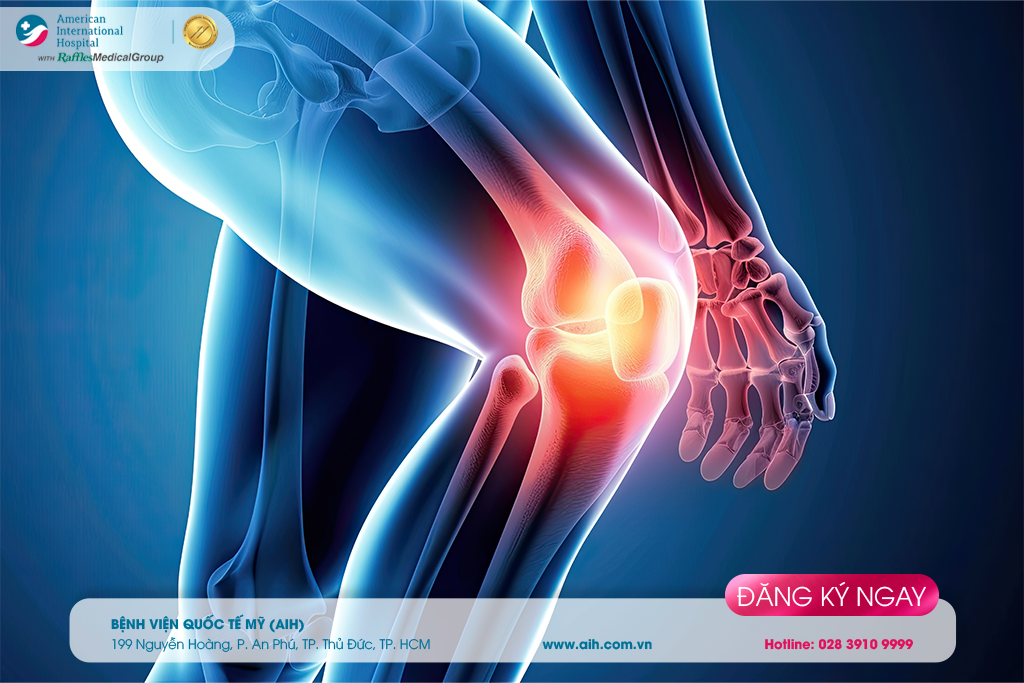
KNEE PAIN: DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Knee pain is a common condition in adults, caused by various factors. Runners or athletes participating in sports that involve jumping or torso rotating are more prone to knee problems. Regardless of whether it is due to aging or sports injuries, this issue can cause discomfort and even knee osteoarthritis for the patient.
► What Is Knee Pain?
The knee is the largest and one of the most complex joints in the body, playing a crucial role in movement. Knee pain refers to discomfort or pain that patients feel around the knee joint, indicating damage inside or around the knee structures, including soft tissues, ligaments, bursae, and tendons. Mild knee pain can be treated at home. However, if the condition worsens, depending on the specific case, surgery might be recommended.
►High-risk Groups for Knee Pain
Several factors might contribute to knee problems, such as:
Overweight: Having excess weight or obesity can place additional stress on the knee joints, even with daily activities such as walking or climbing stairs. This may accelerate cartilage deterioration, raising the risk of osteoarthritis.
Weak or inflexible muscles: The risk of knee injuries is higher with poor muscle strength and flexibility. In contrast, strong muscles can enhance joint stability and protection.
Certain sports or occupations: Some sports exert more pressure on the knees than others. For example, jumping or pivoting in basketball or repetitive knee stress from running can heighten the risk of knee injuries. Occupations that require repetitive movement and pressure on the knee such as construction work or farming can also contribute to the risk.
Previous injuries: People with a history of knee injury are more susceptible to future knee problems.
► Causes of Knee Pain
1. Overexercising
Excessive physical activity, including sports, or heavy exercise, can strain the knee joint. Repeated movements (like frequent jumping or excessive kneeling) may lead to knee pain.
Knee pain can be a manifestation of the following conditions:
Patellofemoral pain (PFPS, also known as runner’s knee)
Osgood-Schlatter disease: Pain and swelling below the knee, common in children and teenagers due to overexercising.
Tendonitis (particularly patellar tendonitis): Higher risks in runners or athletes performing jumping sports.
Bursitis (particularly prepatellar bursitis): Inflammation of the bursae due to overuse, causing severe knee pain.

2. Arthritis
Arthritis can cause joint pain. Knee arthritis is particularly common, manifesting symptoms such as pain, swelling, and joint stiffness. Types of arthritis causing pain include:
Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Post-traumatic arthritis
Repeated trauma.
Sports-related injuries.
Accidents like falls or car crashes.
Knee sprains
Hyperextended knee
Ligament tears (injuries impacting ACL, PCL, MCL, or LCL)
Meniscus tears
Fractures
Dislocations
3. Injuries
Any injury affecting the knee joint can result in pain. Types of knee injuries include:
Repeated trauma.
Sports-related injuries.
Accidents like falls or car crashes.
Common knee injuries causing pain include:
Knee sprains
Hyperextended knee
Ligament tears (injuries impacting ACL, PCL, MCL, or LCL)
Meniscus tears
Fractures
Dislocations
► Symptoms of knee pain
The location and severity of knee pain can vary, depending on its cause. Common signs and symptoms of knee pain are:
Joint swelling and stiffness
Heat and redness on palpation
Weakness or instability
Grinding sounds when moving the knee joints
Inability to fully extend the knee
► Complications of knee pain
Not all knee pain indicates a serious problem. However, in cases of knee injuries such as osteoarthritis, the pain can accelerate, causing joint damage or disability if not properly treated. Moreover, knee injuries, even though mild, can also increase the likelihood of similar accidents in the future.
X-ray: Detects bone fractures and osteoarthritis.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Reveals injuries to soft tissues such as ligaments, tendons, cartilages and muscles.
Computerized Tomography (CT or CAT scan): Identifies injuries or pathologies of the surrounding ligaments or muscles. A CT scan can provide more detailed imaging than a standard X-Ray scan.
Arthroscopy: A diagnostic and minimally invasive treatment procedure used for joint problems. It involves inserting a small, illuminated endoscope (arthroscope) through a cut on the skin (endoscopic gate). The internal joint structures are displayed on the screen, allowing doctors to assess any degenerative changes, inflammation within the joints, pathology, tumor and identify the cause of pain and bone inflammation.

►Treatment of Knee Pain
On most occasions, you can manage knee pain at home with the RICE method:
Rest: Stop any physical activities that cause the pain to prevent worsening the injury.
Ice: Apply ice packs or compress for 15 – 20 minutes every hour on the first day after the injury, and every 3-4 from the second day onward. Wrap the ice with a towel or cloth instead of placing it directly on the skin.
Compression: A knee brace can slow down blood flow to the injured area and reduce swelling. Use a compression bandage or a knee brace.
Elevation: You can elevate your knee with a pillow, blanket or cushion.
2. Painkillers
Most people can take over-the-counter NSAIDs (ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen) or acetaminophen (Tylenol®). However, do not take these medications for 10 consecutive days without consulting a physician, especially if you have kidney or liver disease.
3. Knee Splint
A knee splint can support and maintain proper leg alignment. The splint materials are often hard plastic or metal with padding and straps that wrap around the knee and leg. A healthcare professional can recommend a suitable type of splint and how often it should be worn.
4. Physiotherapy
A healthcare specialist may recommend physiotherapy if you have arthritis or are recovering from an injury. The physical therapist will guide you through stretching and strengthening exercises for the affected knee. This can enhance knee stability and effectively manage pain.
5. Injection
Corticosteroids: Helps reduce arthritis symptoms
Hyaluronic acid: Helps alleviate pain and improve mobility
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma): Reduces inflammation and supports healing process
6. Knee Surgery
Arthroscopy: The most common knee surgery. The surgeon will make small incisions around the patient’s knee, and insert a specialized instrument called an arthroscope, inside the knee to examine the joint in detail.
Joint replacement: The surgeon will replace the damaged knee joint with an artificial one in severe case where the pain and other symptoms significantly affect the ability to stand, walk and move. The surgeon may perform a total or partial knee replacement, depending on the cause and location of the damaged area.
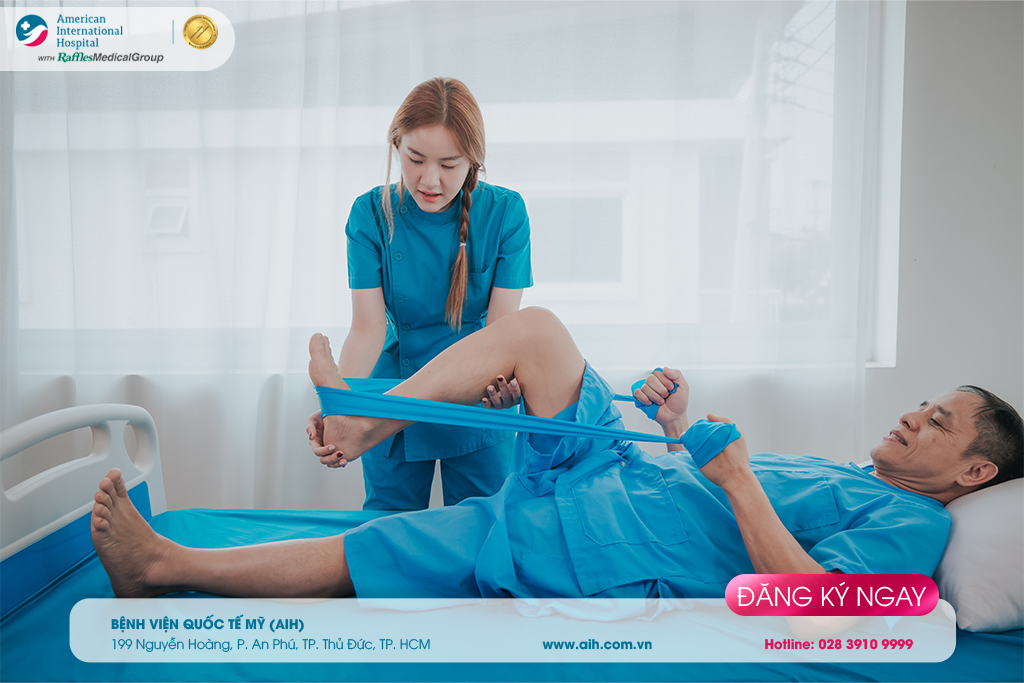

► Prevention of Knee Pain
Maintain a healthy weight: Keeping a proper weight is one of the best ways to prevent knee pain. Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, increasing the risk of injuries and osteoarthritis.
Exercise properly: Ensure that your techniques and movements in sports or physical activities are correct. Avoid high-impact collisions and always warm up before exercising.
Strengthening exercises: Weak muscles are a leading cause of knee injuries. Balance training helps the muscles around the knee function more efficiently. Additionally, engage in exercises that enhance muscle strength and flexibility, such as aerobic exercises, swimming, or cycling.
If you have osteoarthritis, chronic knee pain, or recurrent injuries, you may need to modify your workouts. Consider switching to low-impact activities such as swimming, aerobics, or other gentle exercises for at least a few days each week. In some cases, reducing high-impact activities can effectively protect your knee joints.
--------------------





































































Leave a comment