Notification
Please fill in the information below
Urgent
KNEE PATELLA FRACTURE: HOW TO DIAGNOSE AND TREAT IT?
The patella is a small bone located at the front of the knee joint - where the femur and tibia meet, it acts as a protective shield for the knee joint and connects the muscles in the front of the thigh to the tibia. The lower end of the femur and the back surface of the patella are covered by a smooth substance called articular cartilage. This layer of cartilage allows the bones to slide easily against each other when moving the knee.
A patellar fracture is an injury to the bone that protects the knee, caused by impact or by falling onto the knee. After an injury, the patella may be fractured, displaced, or internally damaged. If a patellar fracture is treated early and correctly, it can heal and restore function well, minimizing the impact on knee flexion and extension.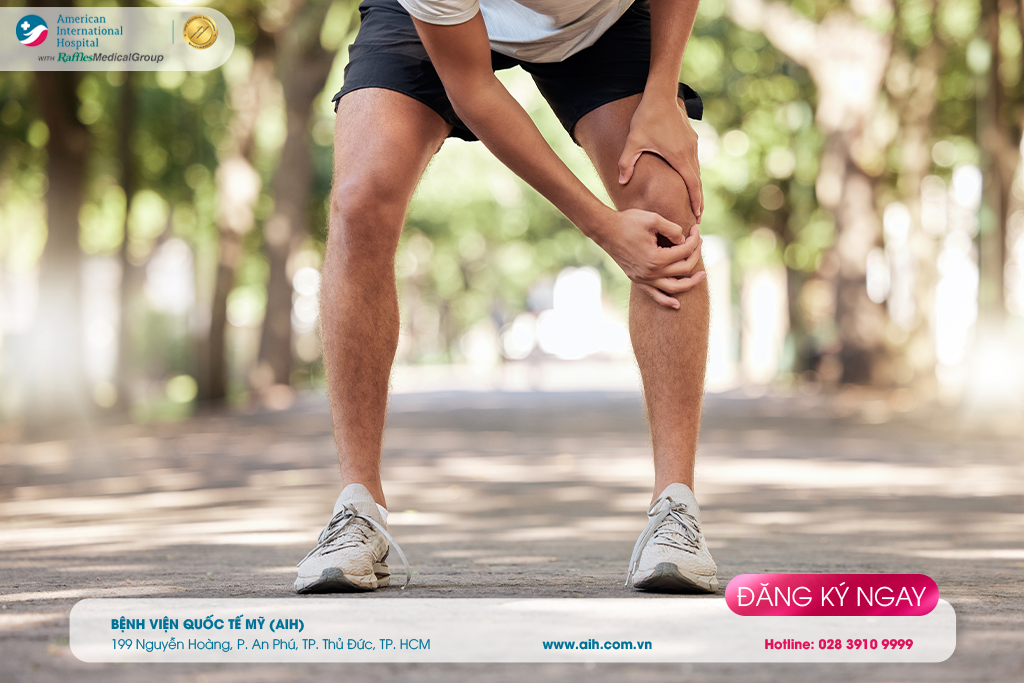
► Classification of patellar fractures
Non-displaced fracture: The bone fragments may still be in contact with each other or separated by a small distance of only 1 - 2 mm. For this type of fracture, the bone is broken but not displaced and can heal well on its own.
Displaced fracture: The bone is broken into fragments and shifted to both sides; this type of fracture requires surgery to reposition the bone fragments back to their original position.
Fracture into many pieces: The patella will be shattered into multiple fragments and may be displaced to surrounding positions or not, depending on the severity of the fracture; it can be stable or unstable.
Fracture with open wound: The broken bone fragments will pierce through the skin or penetrate into other bones, this case will often cause damage to the surrounding soft tissues and take longer to recover.
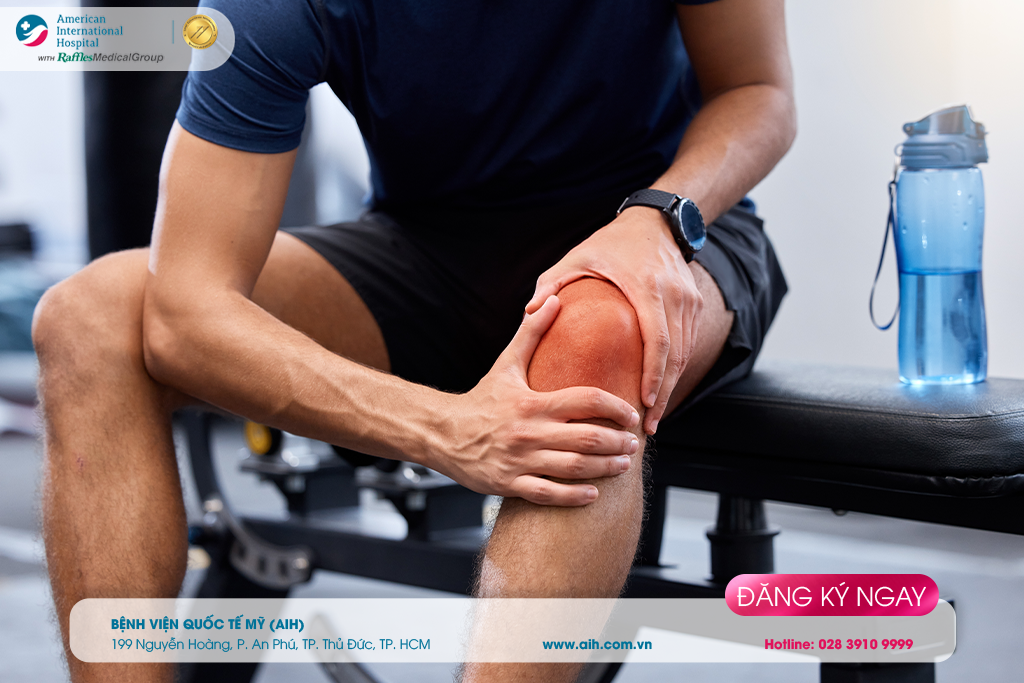
► Individuals prone to patellar fractures
Any age group can suffer from patellar injuries, usually in adults, while it is less common in children.
Patients with osteoarthritis have a high risk of fractures in the knee area.
Older adults, as their bones become brittle and more prone to fractures.
Participation in contact sports such as football, basketball…
Women have a higher likelihood of experiencing knee fractures than men.
Smoking and alcohol consumption affect hormones and bone structure, increasing the risk of fractures.
Patients with a history of previous knee injuries double the risk of encountering similar injuries again.
► The cause of patellar fracture
Fracture of the patella is often caused by impact to the knee, such as:
Falling and landing directly on the knee, especially on hard surfaces like concrete.
Playing sports where the knee can be directly impacted by a ball, bat, etc.
Vehicle accidents causing the knee to hit hard surfaces.
► Typical symptoms
Pain
Swelling
Bruising
Dislocated patella that can be palpated as a bone protruding from the knee
Difficulty in extending or flexing the knee
Deformation of the knee due to severe injury
Inability to walk
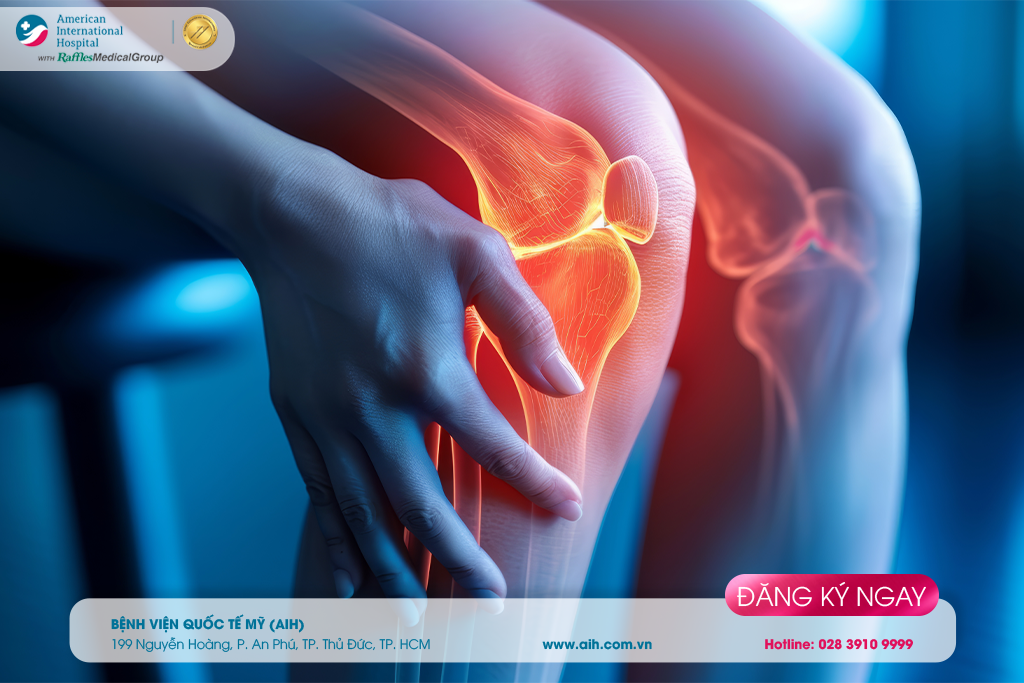
Although after being treated successfully, some patients with patellar fractures may encounter complications as follows:
Post-traumatic arthritis: When the bone has healed, the cartilage surrounding the bone may still be damaged, leading to pain and stiffness in the joints over time. Severe arthritis occurs only in certain patients. Meanwhile, mild to moderate levels of arthritis are referred to as patellar chondromalacia, a condition that is more common.
Muscle weakness: Some patients may experience permanent muscle weakness after a patellar fracture or reduced ability to move the knee, such as extending or flexing the knee.
Prolonged chronic pain: Chronic pain that persists in the front of the knee following a patellar injury is very common. Often, the cause of this pain is difficult to determine, but it may be due to arthritis, stiffness, and muscle weakness.
► Methods of diagnosing
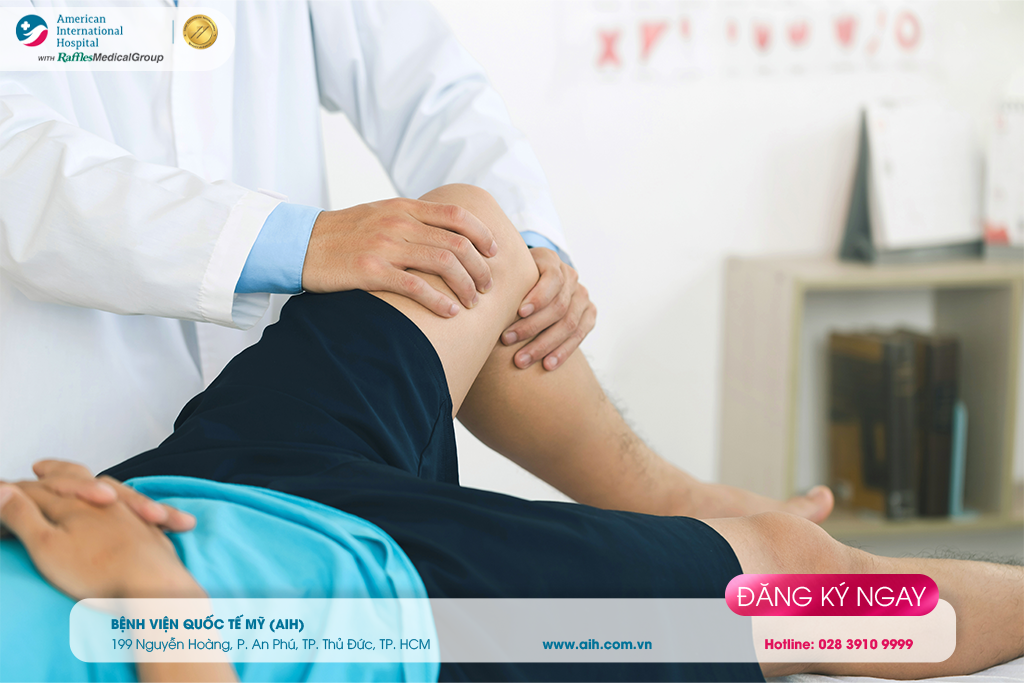
The doctor will ask about the position of the fall, examine the knee to check for open wounds, assess the level of swelling, pain, and joint movement…
Clinical tests: The patient will undergo X-rays or CT scans (for complex injuries) to clearly identify fragments and the degree of displacement.

► Patellar fracture treatment
1. First aid: After the injury, the patient should rest and may apply ice for 15-20 minutes (do not apply directly to the skin) and immobilize the knee with a splint.
2. Treatment: The treatment of patellar fractures depends on the severity and displacement of the fracture site. The results from X-rays (or CT scans) will determine the treatment method.
Conservative treatment: In the case of a non-articular fracture of the anterior surface of the patella, or an articular fracture that is not displaced. A thigh-shin-foot cast is applied, with knee flexed at 30 degrees.
Surgical treatment: In cases of complex fractures, where 2 fragments are separated from each other, or multiple fragments involve the joint surface are unsteady…
After surgery, patients need to undergo physical therapy to aid in a faster recovery process, as a fractured patella can lead to joint stiffness and muscle weakness. Physical therapy may include exercises to strengthen, stretch, and restore movement.
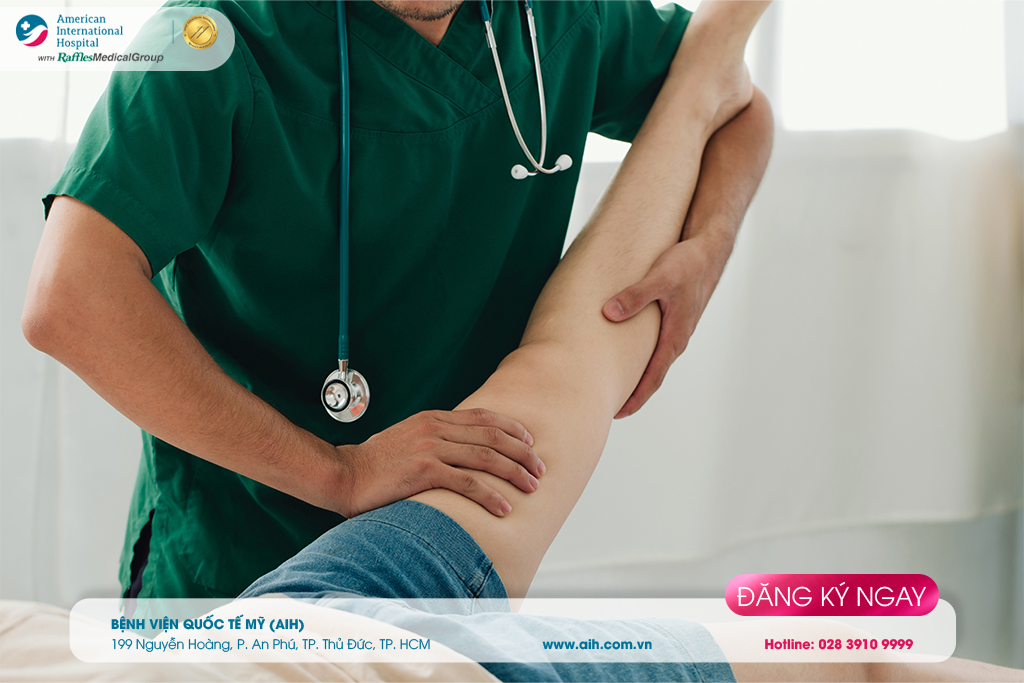
► Effective prevention of patella injuries
Maintaining the health of the legs, musculoskeletal system includes the quadriceps and groin muscles, is very important in effectively preventing patellar injuries. In addition, for those with knee joint conditions, it is necessary to limit activities that put pressure on the knee joint, such as running or lifting heavy objects. It is important to use power-assisted equipment when engaging in activities that require leg strength regularly and to be cautious during daily activities such as participating in traffic and daily living… to minimize the risk of injury.
Search
Latest News
Our Doctor












Leave a comment